circELP2 reverse-splicing biogenesis and function as a pro-fibrogenic factor by targeting mitochondrial quality control pathway
- PMID: 38159063
- PMCID: PMC10844706
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18098
circELP2 reverse-splicing biogenesis and function as a pro-fibrogenic factor by targeting mitochondrial quality control pathway
Abstract
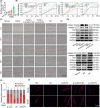
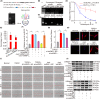
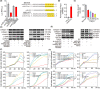
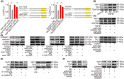
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is considered as a chronic, fibrosing interstitial pneumonia with unknown mechanism. The present work aimed to explore the function, biogenesis and regulatory mechanism of circELP2 in pulmonary fibrosis and evaluate the value of blocking circELP2-medicated signal pathway for IPF treatment. The results showed that heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L initiated reverse splicing of circELP2 resulting in the increase of circELP2 generation. The biogenetic circELP2 activated the abnormal proliferation and migration of fibroblast and extracellular matrix deposition to promote pulmonary fibrogenesis. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that cytoplasmic circELP2 sponged miR-630 to increase transcriptional co-activators Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ). Then, YAP1/TAZ bound to the promoter regions of their target genes, such as mTOR, Raptor and mLST8, which in turn activated or inhibited the genes expression in mitochondrial quality control pathway. Finally, the overexpressed circELP2 and miR-630 mimic were packaged into adenovirus vector for spraying into the mice lung to evaluate therapeutic effect of blocking circELP2-miR-630-YAP1/TAZ-mitochondrial quality control pathway in vivo. In conclusion, blocking circELP2-medicated pathway can alleviate pulmonary fibrosis, and circELP2 may be a potential target to treat lung fibrosis.
Keywords: YAP1/TAZ; circRNA; miRNA; mitochondrial quality control pathway; pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

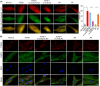
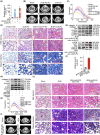
References
-
- Jia Y, Li X, Nan A, et al. Circular RNA 406961 interacts with ILF2 to regulate PM2.5‐induced inflammatory responses in human bronchial epithelial cells via activation of STAT3/JNK pathways. Environ Int. 2020;141:105755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

