Nicorandil Regulates Ferroptosis and Mitigates Septic Cardiomyopathy via TLR4/SLC7A11 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38159178
- PMCID: PMC11147835
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-023-01954-8
Nicorandil Regulates Ferroptosis and Mitigates Septic Cardiomyopathy via TLR4/SLC7A11 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
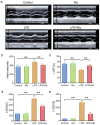
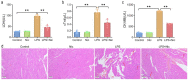
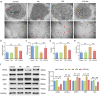
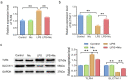
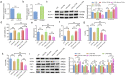
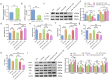
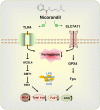
This study mainly explored the role of nicorandil in regulating ferroptosis and alleviating septic cardiomyopathy through toll-like receptor (TLR) 4/solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) signaling pathway. Twenty-four male SD rats were randomly divided into control, Nic (nicorandil), LPS (lipopolysaccharide), and LPS + Nic groups and given echocardiography. A detection kit was applied to measure the levels of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), cardiac troponin I (cTnI), and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB); HE staining and the levels of glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA), total iron, and Fe2+ of myocardial tissues were detected. Moreover, the expression of TLR4 and SLC7A11 were measured by qRT-PCR and the proteins regulating ferroptosis (TLR4, SLC7A11, GPX4, ACSL4, DMT1, Fpn, and TfR1) were checked by western blot. Myocardial cells (H9C2) were induced with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and transfected with si-TLR4 or SLC7A11-OE. Then, the viability, ferroptosis, and TLR4/SLC7A11 signaling pathway of cells were examined. Nicorandil could significantly increase left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (LVEF) while reduce LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Also, it greatly reduced the levels of LDH, cTnI, and CK-MB; alleviated the pathological changes of myocardial injury; notably decreased MDA, total iron, and Fe2+ levels in myocardial tissues; and significantly increased GSH level. Besides, nicorandil obviously raised protein levels of GPX4, Fpn, and SLC7A11, and decreased protein levels of ACSL4, DMT1, TfR1, and TLR4. After knockdown of TLR4 or overexpression of SLC7A11, the inhibition effect of nicorandil on ferroptosis was strengthened in LPS-induced H9C2 cells. Therefore, nicorandil may regulate ferroptosis through TLR4/SLC7A11 signaling, thereby alleviating septic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: ferroptosis; nicorandil; septic cardiomyopathy; toll-like receptor (TLR) 4/solute carrier (SLC) 7A11 signaling pathway..
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role and possible mechanism of the ferroptosis-related SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):531. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04220-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39354361 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin mitigates the lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury in rats by blocking the p53/xCT pathway-mediated ferroptosis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1653-1663. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03367-2. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39153053
-
MiR-31-5p alleviates septic cardiomyopathy by targeting BAP1 to inhibit SLC7A11 deubiquitination and ferroptosis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 May 30;24(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03954-4. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38816686 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Ferroptosis in Cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025 Jun;39(3):595-613. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07514-4. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025. PMID: 37930587 Review.
-
Mechanism of ferroptosis in heart failure: The role of the RAGE/TLR4-JNK1/2 pathway in cardiomyocyte ferroptosis and intervention strategies.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Jul;109:102770. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102770. Epub 2025 May 11. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 40360081 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in muscle diseases and disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects.Bone Res. 2025 Feb 25;13(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00398-6. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 40000618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minocycline alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing the NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 11;14(1):21180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72133-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39261543 Free PMC article.
-
GluOC Induced SLC7A11 and SLC38A1 to Activate Redox Processes and Resist Ferroptosis in TNBC.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;17(5):739. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050739. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075587 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Oxycodone in Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Feb;39(2):e70151. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70151. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39865943 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 mediated signaling axis in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: potential Pharmacological receptor.Inflamm Res. 2025 Apr 29;74(1):76. doi: 10.1007/s00011-025-02037-0. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40299042 Review.
References
-
- Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 2018;392:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Vieillard-Baron A, Caille V, Charron C, Belliard G, Page B, Jardin F. Actual incidence of global left ventricular hypokinesia in adult septic shock. Critical Care Medicine. 2008;36:1701–1706. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, Machado FR, Schachter RD, Finfer S. Recognizing sepsis as a global health priority — A WHO resolution. New England Journal of Medicine. 2017;377:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Balija TM, Lowry SF. Lipopolysaccharide and sepsis-associated myocardial dysfunction. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 2011;24:248–253. - PubMed
-
- Zaky A, Deem S, Bendjelid K, Treggiari MM. Characterization of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: an ongoing challenge. Shock. 2014;41:12–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

