Performance reserves in brain-imaging-based phenotype prediction
- PMID: 38159275
- PMCID: PMC11215805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113597
Performance reserves in brain-imaging-based phenotype prediction
Abstract
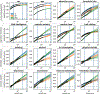
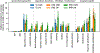
This study examines the impact of sample size on predicting cognitive and mental health phenotypes from brain imaging via machine learning. Our analysis shows a 3- to 9-fold improvement in prediction performance when sample size increases from 1,000 to 1 M participants. However, despite this increase, the data suggest that prediction accuracy remains worryingly low and far from fully exploiting the predictive potential of brain imaging data. Additionally, we find that integrating multiple imaging modalities boosts prediction accuracy, often equivalent to doubling the sample size. Interestingly, the most informative imaging modality often varied with increasing sample size, emphasizing the need to consider multiple modalities. Despite significant performance reserves for phenotype prediction, achieving substantial improvements may necessitate prohibitively large sample sizes, thus casting doubt on the practical or clinical utility of machine learning in some areas of neuroimaging.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; accuracy limits; brain imaging; machine learning; multimodal imaging; sample size; scaling behavior.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved prediction of brain age using multimodal neuroimaging data.Hum Brain Mapp. 2020 Apr 15;41(6):1626-1643. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24899. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020. PMID: 31837193 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Machine Learning Models for Brain Age Prediction Using Six Imaging Modalities on Middle-Aged and Older Adults.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;23(7):3622. doi: 10.3390/s23073622. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050682 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating across neuroimaging modalities boosts prediction accuracy of cognitive ability.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Mar 5;17(3):e1008347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008347. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33667224 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Neuroimaging: Basic Concepts and Classification of Neuropsychiatric Diseases.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2019 Jan;50(1):20-33. doi: 10.1177/1550059418782093. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 29925268 Review.
-
Towards a brain-based predictome of mental illness.Hum Brain Mapp. 2020 Aug 15;41(12):3468-3535. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25013. Epub 2020 May 6. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020. PMID: 32374075 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances and challenges in neuroimaging-based pain biomarkers.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Oct 15;5(10):101784. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101784. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39383872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Group-to-individual generalizability and individual-level inferences in cognitive neuroscience.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025 Feb;169:106024. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2025.106024. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025. PMID: 39889869 Review.
-
Prediction of cognitive performance differences in older age from multimodal neuroimaging data.Geroscience. 2024 Feb;46(1):283-308. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00831-4. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 37308769 Free PMC article.
-
Do Transformers and CNNs Learn Different Concepts of Brain Age?Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Jun 1;46(8):e70243. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70243. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025. PMID: 40489428 Free PMC article.
-
Voxel-Wise or Region-Wise Nuisance Regression for Functional Connectivity Analyses: Does It Matter?Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Aug 15;46(12):e70323. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70323. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025. PMID: 40838474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VFJ, Simpson JP, Kane AD, Menon DK, Rueckert D, and Glocker B. (2017). Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 36, 61–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

