Recruitment of trimeric eIF2 by phosphatase non-catalytic subunit PPP1R15B
- PMID: 38159565
- PMCID: PMC7615683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.12.011
Recruitment of trimeric eIF2 by phosphatase non-catalytic subunit PPP1R15B
Abstract
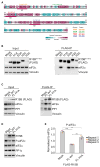
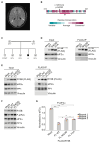
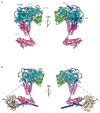
Regulated protein phosphorylation controls most cellular processes. The protein phosphatase PP1 is the catalytic subunit of many holoenzymes that dephosphorylate serine/threonine residues. How these enzymes recruit their substrates is largely unknown. Here, we integrated diverse approaches to elucidate how the PP1 non-catalytic subunit PPP1R15B (R15B) captures its full trimeric eIF2 substrate. We found that the substrate-recruitment module of R15B is largely disordered with three short helical elements, H1, H2, and H3. H1 and H2 form a clamp that grasps the substrate in a region remote from the phosphorylated residue. A homozygous N423D variant, adjacent to H1, reducing substrate binding and dephosphorylation was discovered in a rare syndrome with microcephaly, developmental delay, and intellectual disability. These findings explain how R15B captures its 125 kDa substrate by binding the far end of the complex relative to the phosphosite to present it for dephosphorylation by PP1, a paradigm of broad relevance.
Keywords: PP1; PPP1R15B; intrinsically disordered proteins; mass spectrometry; missense variants; nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy; phosphatase; structural proteomics; syndrome.
Copyright © 2023 MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cohen P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:E127–E130. - PubMed
-
- Humphrey SJ, James DE, Mann M. Protein phosphorylation: A major switch mechanism for metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26:676–687. - PubMed
-
- Chen MJ, Dixon JE, Manning G. Genomics and evolution of protein phosphatases. Sci Signal. 2017;10:eaag1796. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y. Serine/threonine phosphatases: mechanism through structure. Cell. 2009;139:468–484. - PubMed
-
- Brautigan DL. Protein Ser/Thr phosphatases - the ugly ducklings of cell signalling. FEBS Journal. 2013;280:324–345. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

