Genetic Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Control Study
- PMID: 38160213
- PMCID: PMC11427610
- DOI: 10.1007/s10528-023-10648-7
Genetic Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Control Study
Abstract
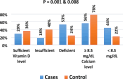
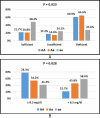
Vitamin D effects are mediated by vitamin D receptors (VDRs), which are influenced by various genetic polymorphisms, including ApaI and BsmI. These polymorphisms have been linked to several diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aimed to compare the frequency and association of VDR ApaI and BsmI gene polymorphisms, serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D (25-(OH)-D) levels, and calcium (Ca) levels between a RA group and a matched healthy control group. In one hundred RA patients and fifty healthy controls, the genotypes of the VDR ApaI and BsmI gene polymorphisms were analyzed using polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphisms (PCR-RFLP). Both Serum 25-(OH)-D level and calcium level were measured in the two groups. There was no significant difference between the cases and controls regarding the VDR ApaI gene polymorphism (p = 0.89). A significant difference was observed between the cases and controls in terms of the VDR BsmI gene polymorphism (p = < 0.001). The serum levels of 25-(OH)-D and calcium were significantly lower in the RA group compared to the control group (p = 0.04 and < 0.001 respectively). Significantly higher serum vitamin D levels were associated with the aa genotype (p = 0.007). Significantly increased calcium levels were associated with the AA genotype (p = 0.02). No significant difference was found among BsmI polymorphisms regarding vitamin D and Ca levels (p = 0.25 and 0.87 respectively). Vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphism but not ApaI polymorphism could be a marker of RA susceptibility. Vitamin D and Ca levels are negatively affected by RA. Vitamin D receptor gene ApaI polymorphism contributes to vitamin D and Ca levels.
Keywords: ApaI; BsmI; Calcium; Rheumatoid arthritis; Vitamin D.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Association of polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in children with autism spectrum disorder.Gene. 2016 Aug 22;588(2):109-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 May 4. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27155524
-
Vitamin D receptor TaqI and ApaI polymorphisms: a comparative study in patients with Behçet's disease and Rheumatoid arthritis in Tunisian population.Cell Immunol. 2014 Jul;290(1):66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2014.05.002. Epub 2014 May 17. Cell Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24880677
-
Vitamin D and VDR Gene Polymorphisms' Association with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Lithuanian Population.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Apr 3;57(4):346. doi: 10.3390/medicina57040346. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33916688 Free PMC article.
-
Associations among four polymorphisms (BsmI, FokI, TaqI and ApaI) of vitamin D receptor gene and end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis.Arch Med Res. 2015 Jan;46(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2014.11.017. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Arch Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25434518 Review.
-
[Research progress on polymorphism of vitamin D and its receptor gene and susceptibility to bone tuberculosis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2025 Feb 25;38(2):211-6. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.20240312. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2025. PMID: 40033625 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Interaction Between Vitamin D Metabolism Genetic Variants: Association with Hypovitaminosis D, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Its Clinical Disease Activity.Genes (Basel). 2025 Aug 18;16(8):967. doi: 10.3390/genes16080967. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40870018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Nahas Z, Fawzy M, Menyawi E, Shaker M, O., Ragab G (2017) 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in Egyptian patients with Behçet’s Disease: a pilot study. Int J Clin Rheumatol 12:20–27
-
- Alamanos Y, Drosos AA (2005) Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 4(3):130–136 - PubMed
-
- Albedri Khudair Z, Derwibee Fadya EAAA A (2020) Serum calcium and serum alkaline phosphatase levels and their correlations with Disease Activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Medico-legal Update 20:7
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham III, Cohen CO, M. D (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthr Rhuem 62(9):2569–2581 - PubMed
-
- Bagheri-Hosseinabadi Z, Imani D, Yousefi H, Abbasifard M (2020) Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphism and risk of rheumatoid arthritis (RA): systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 39:3555–3569 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

