When to Do Selective Patellar Resurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Decision-Making Algorithm Based on Pre-operative and Intra-operative Findings
- PMID: 38161405
- PMCID: PMC10754792
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-023-01039-6
When to Do Selective Patellar Resurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Decision-Making Algorithm Based on Pre-operative and Intra-operative Findings
Abstract
Background: Persistent anterior knee pain post total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a significant cause of patient dissatisfaction. Selective patellar resurfacing is commonly practiced for primary total knee replacement (TKR) but there is a paucity in literature regarding its decision making.
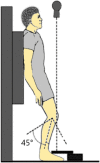
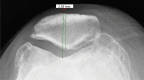
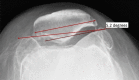
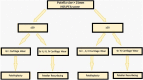
Study objective: This study aims to develop a decision-making algorithm for selective patellar resurfacing using Hospital for Special Surgery Patello-femoral Assessment score (HSS PFA score), weight-bearing patellofemoral X-ray, and intraoperative cartilage wear assessment based on the Outerbridge classification.
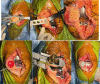
Materials and methods: This prospective study enrolled 65 patients, assessing preoperative factors including HSS PFA score and Baldini view radiography. Intraoperative cartilage wear was categorized using the Outerbridge classification. Preoperative findings were correlated with intraoperative outcomes through statistical analysis, leading to the development of a predictive algorithm. The efficiency of algorithm was assessed at 3-year follow-up using HSS PFA score.
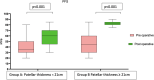
Results: A significant negative correlation (r = - 0.272, p = 0.029) was observed between HSS PFA score and cartilage wear. However, no significant relationships were established between HSS PFA score and Baldini view observations, including radiological tilt (p = 0.517) and displacement (p = 0.277). Intraoperative cartilage wear versus patellar tilt (p = 0.65) and displacement (p = 0.837) also yielded non-significant results. Three-year follow-up examinations revealed no complications and significant HSS PFA score improvements in all patients.
Conclusion: The requirement for patellar resurfacing can be predicted using a combination of preoperative parameter such as HSS PFA score and the intra-operative cartilage wear. We put forward an algorithm based on above findings to aid in the decision making.
Keywords: Baldini view; HSS patella femoral score; Selective patellar resurfacing.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patellar Resurfacing Does Not Improve Clinical Outcome in Patients with Symptomatic Tricompartmental Knee Osteoarthritis. An RCT Study of 40 Patients Receiving Primary Cruciate Retaining Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Knee Surg. 2021 Dec;34(14):1503-1509. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1710369. Epub 2020 May 20. J Knee Surg. 2021. PMID: 32434236 Clinical Trial.
-
Patellar resurfacing in posterior cruciate ligament retaining total knee arthroplasty (PATRES): design of a randomized controlled clinical trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014 Oct 29;15:358. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-358. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014. PMID: 25351573 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative patellar bone marrow lesions with full thickness cartilage defects correlate with residual anterior knee pain in total knee arthroplasty without patellar resurfacing.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 Nov;31(11):5048-5056. doi: 10.1007/s00167-023-07551-4. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 37695390
-
Better outcomes with patellar resurfacing during primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis study.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 Oct;139(10):1445-1454. doi: 10.1007/s00402-019-03246-z. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019. PMID: 31367842 Review.
-
Patellar resurfacing complications in total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2014 Feb;38(2):313-7. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2244-3. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24363045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fragility analysis and systematic review of patellar resurfacing versus non-patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty.J Exp Orthop. 2024 Aug 6;11(3):e12113. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.12113. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Exp Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39108460 Free PMC article.
-
Patellar Resurfacing in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Contentious Matter.Cureus. 2024 Oct 6;16(10):e70936. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70936. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39502955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourlez J, Canovas F, Duflos C, Dagneaux L. Are modern knee outcomes scores appropriate for evaluating patellofemoral degeneration in osteoarthritis? Evaluation of the ceiling and floor effects in knee outcomes scores. Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Surgery & Research. 2019;105(4):599–603. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.01.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shih HN, Shih LY, Wong YC, Hsu RWW. Long-term changes of the nonresurfaced patella after total knee arthroplasty. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series A. 2004;86:935–939. - PubMed
-
- Patel VV, Hall K, Ries M, Lindsey C, Ozhinsky E, Lu Y, Majumdar S. Magnetic resonance imaging of patellofemoral kinematics with weight-bearing. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series A. 2003;85:2419–2424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
