Micro/nanosystems for controllable drug delivery to the brain
- PMID: 38161522
- PMCID: PMC10757293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xinn.2023.100548
Micro/nanosystems for controllable drug delivery to the brain
Abstract
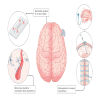
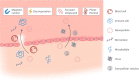
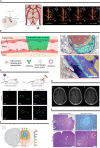
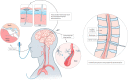
Drug delivery to the brain is crucial in the treatment for central nervous system disorders. While significant progress has been made in recent years, there are still major challenges in achieving controllable drug delivery to the brain. Unmet clinical needs arise from various factors, including controlled drug transport, handling large drug doses, methods for crossing biological barriers, the use of imaging guidance, and effective models for analyzing drug delivery. Recent advances in micro/nanosystems have shown promise in addressing some of these challenges. These include the utilization of microfluidic platforms to test and validate the drug delivery process in a controlled and biomimetic setting, the development of novel micro/nanocarriers for large drug loads across the blood-brain barrier, and the implementation of micro-intervention systems for delivering drugs through intraparenchymal or peripheral routes. In this article, we present a review of the latest developments in micro/nanosystems for controllable drug delivery to the brain. We also delve into the relevant diseases, biological barriers, and conventional methods. In addition, we discuss future prospects and the development of emerging robotic micro/nanosystems equipped with directed transportation, real-time image guidance, and closed-loop control.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Microfluidics in drug delivery: review of methods and applications.Pharm Dev Technol. 2023 Jan;28(1):61-77. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2022.2162543. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Pharm Dev Technol. 2023. PMID: 36592376 Review.
-
Advanced Drug Delivery Micro- and Nanosystems for Cardiovascular Diseases.Molecules. 2022 Sep 9;27(18):5843. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185843. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Development of Drug Delivery Systems through Microfluidics: From Synthesis to Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 17;14(2):434. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020434. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of controlled drug delivery using microfluidic platforms.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018 Mar 15;128:3-28. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018. PMID: 28919029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Nanotechnology-mediated Herbal Nanosystems for Ophthalmic Drug.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2024;12(3):229-250. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666230816090046. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37587812 Review.
Cited by
-
Landscape of human organoids: Ideal model in clinics and research.Innovation (Camb). 2024 Apr 1;5(3):100620. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2024.100620. eCollection 2024 May 6. Innovation (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38706954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotherapeutics for Meningitis: Enhancing Drug Delivery Across the Blood-Brain Barrier.Biomimetics (Basel). 2025 Jan 3;10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics10010025. Biomimetics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39851741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Drug Delivery Systems Based on Nanoparticles for Improved Glioblastoma Therapy: Addressing Challenges and Investigating Opportunities.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;17(4):701. doi: 10.3390/cancers17040701. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid films loaded with 5-fluorouracil and Reglan for synergistic treatment of colon cancer via asynchronous dual-drug delivery.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 13;12:1398730. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398730. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38938981 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise-targeting and hypoxia-responsive liposome AMVY@NPs carrying siYAP and verteporfin for glioblastoma therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 20;22(1):495. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02776-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39164753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vigo D., Thornicroft G., Atun R. Estimating the true global burden of mental illness. Lancet Psychiatr. 2016;3:171–178. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

