A rare case: IgG4-related chronic inflammatory disease with kidney involvement
- PMID: 38161639
- PMCID: PMC10753643
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.8164
A rare case: IgG4-related chronic inflammatory disease with kidney involvement
Abstract
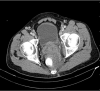
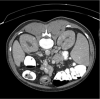
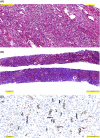
IgG4-related disease is an inflammatory, multisystemic disease that affects the immune system. The disease progresses to fibrosis due to inflammation. Retroperitoneal fibrosis is a serious complication. Pancreas, biliary tract, glands, thyroid, lymph nodes, etc. may be involved. Prognosis is usually subacute, and seen in middle age and advanced men. It is characterized histopathologically by IgG4 positive plasma cells, lymphoplasmocytic cell infiltration, and storiform fibrosis. In our case, we evaluated a patient who referred to our clinic from an external center with the complaints of generalized pain, itching, tearing and redness in eyes, involvement of bilateral large joints, and impaired renal function. Diagnosis, treatment and management of the disease are important. Response to glucocorticoid therapy is good.
Keywords: IgG4 related disease; acute kidney injury; tubulointerstitial nephritis.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest between authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Case report: IgG4-related renal disease co-existing with retroperitoneal fibrosis.Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Apr;9(2):794-799. doi: 10.21037/tau.2020.02.06. Transl Androl Urol. 2020. PMID: 32420186 Free PMC article.
-
Retroperitoneal fibrosis associated with orbital pseudotumor without evidence of IgG4: A case report with review of literature.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2019 Feb;8(1):29-35. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2018.01075. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2019. PMID: 30881855 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Rosai-Dorfman Disease Mimicking IgG4-related Disease.Intern Med. 2022 Apr 1;61(7):1027-1032. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8046-21. Epub 2021 Sep 18. Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34544952 Free PMC article.
-
Renal involvement in IgG4-related disease.Presse Med. 2020 Apr;49(1):104017. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2020.104017. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Presse Med. 2020. PMID: 32234380 Review.
-
Current Concept of IgG4-Related Disease.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;401:1-17. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_47. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28091932 Review.
References
-
- Karim AF, Bansie RD, Rombach SM, et al. The treatment outcomes in IgG4‐related disease. Neth J Med. 2018;76(6):275‐285. - PubMed
-
- Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European league against rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4‐related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(1):77‐87. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

