Impact of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction on Myocardial Strain in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 38161778
- PMCID: PMC10756320
- DOI: 10.4103/jcecho.jcecho_28_23
Impact of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction on Myocardial Strain in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
Background: This research aimed to evaluate the role of coronary microvascular dysfunction in alteration of left ventricular (LV) myocardial deformation.
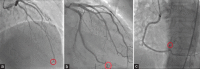
Materials and methods: This observational study involved 50 patients with LV ejection fraction (LVEF) >50% and coronary microvascular dysfunction (diagnosed by coronary angiography). TIMI frame count (TFC) was calculated for each patient. They were classified into 2 groups: 30 patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (cases group) and 20 patients without HF (control group). Speckle tracking echocardiography was used to evaluate LV deformation.
Results: The mean age of the studied patients was 58.8 ± 8 years. The frequency of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia were significantly higher in cases than controls. Cases had significant higher BMI (30 ± 4.48 vs. 27.3 ± 3.94 kg/m2, P=0.029). The total TFC in cases was 97.1 ± 22.9 and in controls was 79 ± 18.5, and this difference was statistically significant (P=0.005). Significantly decreased LV global strain was observed in HFpEF cases than in controls (-17.6 ± 2.14 % versus -19.5 ± 1.98%, P < 0.001). In cases with a higher TFC, the LV global strain decrease was more pronounced. There was a significant correlation between the LV global strain and total TFC (r=-0.470 and P=0.009).
Conclusion: Patients with HFpEF exhibited higher total TFC reflecting more affected coronary microvasculature. Those patients had reduced LV global strain. Coronary microvascular dysfunction probably leads to alteration of myocardial performance.
Keywords: Coronary microvascular dysfunction; TIMI frame count; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; left ventricular longitudinal strain.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Cardiovascular Echography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation between longitudinal strain analysis and coronary microvascular dysfunction in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Microcirculation. 2020 Apr;27(3):e12605. doi: 10.1111/micc.12605. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Microcirculation. 2020. PMID: 31889374
-
Impaired systolic function by strain imaging in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Feb 11;63(5):447-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.09.052. Epub 2013 Oct 30. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24184245 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Myocardial deformation assessed among heart failure entities by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging.ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Apr;8(2):890-897. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13193. Epub 2021 Feb 4. ESC Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 33539681 Free PMC article.
-
A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Jul 23;62(4):263-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.02.092. Epub 2013 May 15. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23684677 Review.
-
Assessment of left and right ventricular diastolic and systolic functions using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in patients with coronary slow-flow phenomenon.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 23;10(2):e0117979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117979. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25706989 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Influence of Non-Dipping Pattern of Blood Pressure in Gestational Hypertension on Early Onset of Hypertension Later in Life-Single Center Experience in Very-High-Risk Southeast and Central European Country.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 21;25(20):11324. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011324. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Riet EE, Hoes AW, Limburg A, Landman MA, van der Hoeven H, Rutten FH. Prevalence of unrecognized heart failure in older persons with shortness of breath on exertion. Eur J Heart Fail. 2014;16:772–7. - PubMed
-
- Koh AS, Tay WT, Teng TH, Vedin O, Benson L, Dahlstrom U, et al. Acomprehensive population-based characterization of heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19:1624–34. - PubMed
-
- Chioncel O, Lainscak M, Seferovic PM, Anker SD, Crespo-Leiro MG, Harjola VP, et al. Epidemiology and one-year outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved, mid-range and reduced ejection fraction:An analysis of the ESC heart failure long-term registry. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19:1574–85. - PubMed
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3599–726. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
