Toward a holographic brain paradigm: a lipid-centric model of brain functioning
- PMID: 38161798
- PMCID: PMC10757614
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1302519
Toward a holographic brain paradigm: a lipid-centric model of brain functioning
Abstract
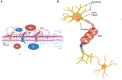
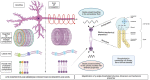
Due to the stimulation of neuronal membrane dipoles by action potentials, under suitable conditions coherent dipole oscillations can be formed. We argue that these dipole oscillations satisfy the weak Bose-Einstein condensate criteria of the Froehlich model of biological coherence. They can subsequently generate electromagnetic fields (EMFs) propagating in the inter-neuronal space. When neighboring neurons fire synchronously, EMFs can create interference patterns and hence form holographic images containing analog information about the sensory inputs that trigger neuronal activity. The mirror pattern projected by EMFs inside the neuron can encode information in the neuronal cytoskeleton. We outline an experimental verification of our hypothesis and its consequences for anesthesia, neurodegenerative diseases, and psychiatric states.
Keywords: action potential; consciousness; electromagnetic field; holography; lipid membrane.
Copyright © 2023 Cavaglià, Deriu and Tuszynski.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Collapse and revival of the matter wave field of a Bose-Einstein condensate.Nature. 2002 Sep 5;419(6902):51-4. doi: 10.1038/nature00968. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12214228
-
Sensory transduction of weak electromagnetic fields: role of glutamate neurotransmission mediated by NMDA receptors.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 31;258:184-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.009. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24239718
-
Extending Integrate-and-Fire Model Neurons to Account for the Effects of Weak Electric Fields and Input Filtering Mediated by the Dendrite.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Nov 28;12(11):e1005206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005206. eCollection 2016 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27893786 Free PMC article.
-
Millimeter (MM) wave and microwave frequency radiation produce deeply penetrating effects: the biology and the physics.Rev Environ Health. 2021 May 26;37(2):247-258. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2020-0165. Print 2022 Jun 27. Rev Environ Health. 2021. PMID: 34043892 Review.
-
Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields stimulation modulates autoimmunity and immune responses: a possible immuno-modulatory therapeutic effect in neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2016 Dec;11(12):1888-1895. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.195277. Neural Regen Res. 2016. PMID: 28197174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Holographic Brain Theory: Super-Radiance, Memory Capacity and Control Theory.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 18;25(4):2399. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042399. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397075 Free PMC article.
-
The Sentient Cell: Implications for Osteopathic Medicine.Cureus. 2024 Feb 20;16(2):e54513. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54513. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38384870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberts B, Wilson J, Hunt T. Molecular biology of the cell. 5th ed. New York: Garland Science; (2008).
-
- Appali R., Van Rienen U., Heimburg T. (2012). A comparison of the Hodgkin–Huxley model and the soliton theory for the action potential in nerves. Adv. Planar Lipid Bilayers Liposomes 16, 275–299. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396534-9.00009-X - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

