Simulated vestibular spatial disorientation mouse model under coupled rotation revealing potential involvement of Slc17a6
- PMID: 38162025
- PMCID: PMC10757040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108498
Simulated vestibular spatial disorientation mouse model under coupled rotation revealing potential involvement of Slc17a6
Abstract
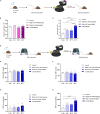
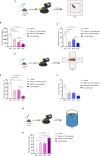
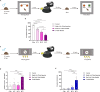
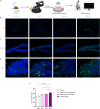
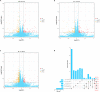
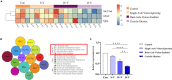
Spatial disorientation (SD) is the main contributor to flight safety risks, but research progress in animals has been limited, impeding a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms of SD. This study proposed a method for constructing and evaluating a vestibular SD mouse model, which adopted coupled rotational stimulation with visual occlusion. Physiological parameters were measured alongside behavioral indices to assess the model, and neuronal changes were observed through immunofluorescent staining. The evaluation of the model involved observing decreased colonic temperature and increased arterial blood pressure in mice exposed to SD, along with notable impairments in motor and cognitive function. Our investigation unveiled that vestibular SD stimulation elicited neuronal activation in spatially associated cerebral areas, such as the hippocampus. Furthermore, transcriptomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis revealed the potential involvement of Slc17a6 in the mechanism of SD. These findings lay a foundation for further investigation into the molecular mechanisms underlying SD.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Natural sciences; Neuroscience; Physiology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Auditory Verbal Working Memory Load Effects on a Simulator-Induced Spatial Disorientation Event.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2019 Jun 1;90(6):531-539. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.5277.2019. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2019. PMID: 31101138 Clinical Trial.
-
Selective Auditory Attention and Spatial Disorientation Cues Effect on Flight Performance.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2018 Nov 1;89(11):976-984. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.5153.2018. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2018. PMID: 30352650
-
Galvanic vestibular stimulation to counteract leans illusion: comparing step and ramped waveforms.Ergonomics. 2023 Apr;66(4):432-442. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2022.2093403. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Ergonomics. 2023. PMID: 35730683
-
Sensorial countermeasures for vestibular spatial disorientation.Aviat Space Environ Med. 2014 May;85(5):563-7. doi: 10.3357/asem.3735.2014. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2014. PMID: 24834571 Review.
-
Detection of unrecognized spatial disorientation: A theoretical perspective.Technol Health Care. 2022;30(S1):469-480. doi: 10.3233/THC-THC228043. Technol Health Care. 2022. PMID: 35124621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lessard C.S. Spatial disorientation: dealing with aeronautical illusions. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2000;19:25–27. - PubMed
-
- Meeks R.K., Anderson J., Bell P.M. 2023. Physiology of Spatial Orientation. - PubMed
-
- Gibb R., Ercoline B., Scharff L. Spatial disorientation: Decades of pilot fatalities. Aviat Space Environ. Med. 2011;82:717–724. - PubMed
-
- Newman R.L., Rupert A.H. The Magnitude of the Spatial Disorientation Problem in Transport Airplanes. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2020;91:65–70. - PubMed
-
- Pennings H.J.M., Oprins E.A.P.B., Wittenberg H., Houben M.M.J., Groen E.L. Spatial Disorientation Survey Among Military Pilots. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2020;91:4–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

