[A Preliminary Study on the Plasma Metabolomic Profiles of Patients Suffering From Acute Diquat Poisoning]
- PMID: 38162068
- PMCID: PMC10752779
- DOI: 10.12182/20231160601
[A Preliminary Study on the Plasma Metabolomic Profiles of Patients Suffering From Acute Diquat Poisoning]
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the plasma metabolomic features of patients suffering from acute diquat (DQ) poisoning and to explore the molecular mechanism and potential biomarkers of DQ poisoning.
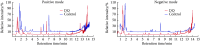
Methods: A total of 7 patients suffering from acute DQ poisoning were enrolled in the DQ poisoning group. The poisoning of these patients occurred within a 12-h window at the time of enrollment. Meanwhile, 7 healthy immediate family members of the patients were enrolled as the normal controls. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was used to perform non-targeted metabolomic profiling of the plasma samples and to screen and identify differential metabolites and metabolic pathways.
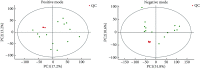
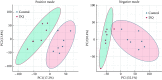
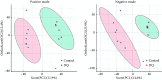
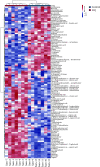
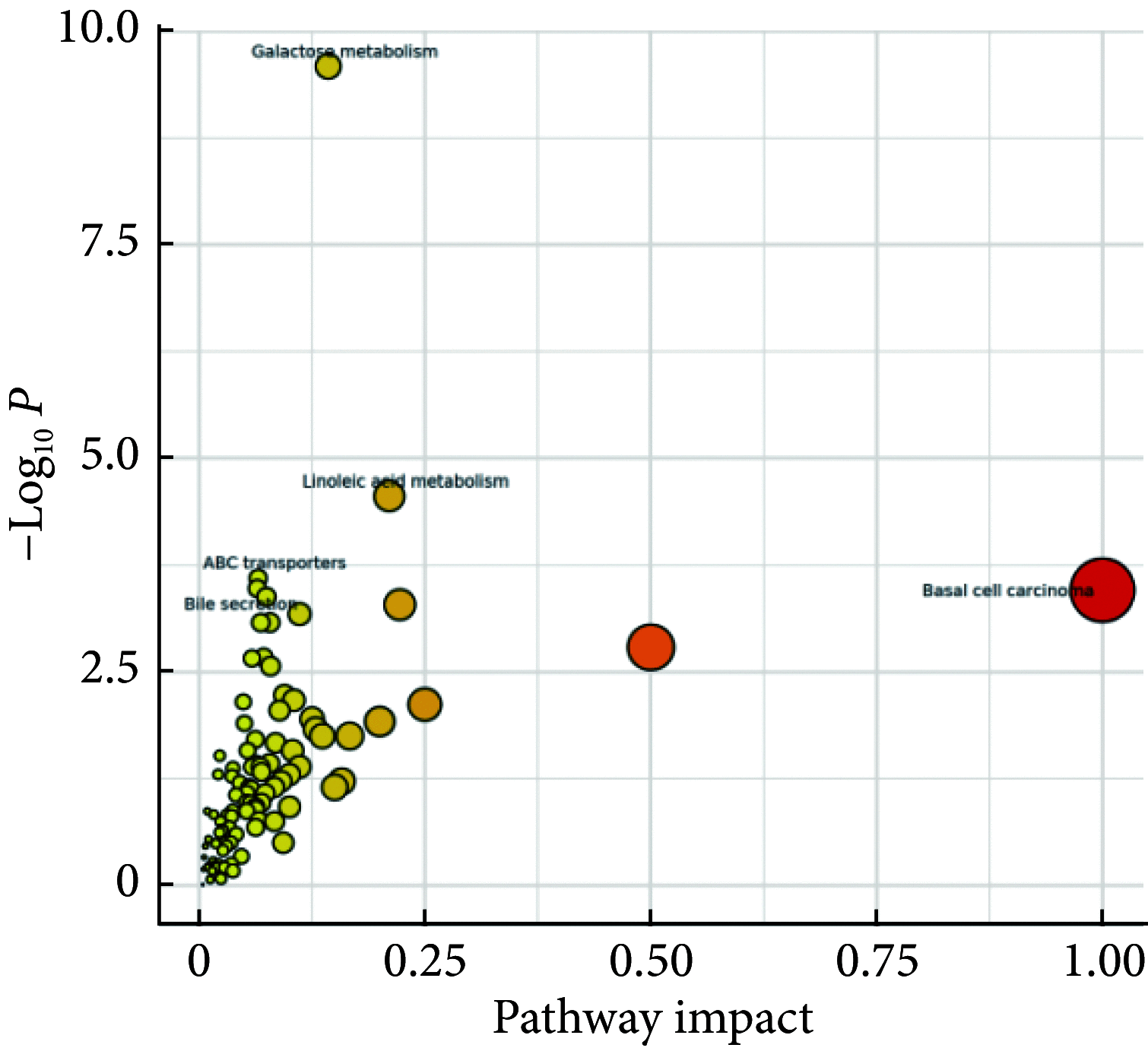
Results: A total of 104 metabolites were screened and identified (P<0.05 and the variable importance in the projection [VIP]>1). Compared with those of the control group, 61 metabolites, such as sorbitol and galactitol, were up-regulated, and 43 metabolites, such as myo-inositol and gamma-glutamylcysteine, were down-regulated in the DQ poisoning group. Pathway enrichment analysis revealed changes in 11 metabolic pathways, including those for galactose metabolism and linoleic acid metabolism (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Metabolomics analysis of plasma samples from DQ poisoning patients shows that DQ mainly interferes with the metabolism of energy, amino acids, and lipids, thus causing metabolic disorders. Some potential biomarkers closely associated with oxidative stress and organ damage of the liver, kidney, and nervous system have been identified.
目的: 分析急性敌草快(diquat, DQ)中毒患者血浆代谢组学特征,探讨中毒的分子机制和潜在生物标志物。
方法: 收集7例12 h内急性DQ中毒的患者作为DQ中毒组,7例同时期患者直系健康家属为正常对照组。采用液相色谱-质谱联用(liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, LC-MS)的非靶向代谢组学技术对血浆样本进行检测,筛选和鉴定差异代谢物及代谢通路。
结果: 筛选和鉴定出104个代谢物(P<0.05和VIP>1),与对照组相比,DQ中毒患者血浆中山梨醇、半乳糖醇等61个代谢物上调,肌-肌醇、γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸等43个代谢物下调。通路富集分析发现有半乳糖代谢、亚油酸代谢等11条代谢通路发生变化(P<0.05)。
结论: 通过对DQ中毒患者血浆样本的代谢组学分析,发现DQ主要干扰了能量、氨基酸、脂质代谢,造成代谢紊乱,并发现若干与氧化应激、肝、肾、神经系统等器官损伤密切相关的潜在生物标志物。
Keywords: Diquat; Metabolomics; Plasma; Poisoning.
© 2023《四川大学学报(医学版)》编辑部 版权所有Copyright ©2023 Editorial Board of Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Sciences).
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolomics profile of plasma in acute diquat-poisoned patients using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.Food Chem Toxicol. 2023 Jun;176:113765. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2023.113765. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37023971
-
Prognostic value of plasma diquat concentration in patients with acute oral diquat poisoning: a retrospective study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 4;12:1333450. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1333450. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38894984 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical features of 86 cases of acute diquat poisoning].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Mar;34(3):301-305. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220128-00105. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35574750 Chinese.
-
Construction of a risk prediction model of diquat poisoning based on clinical indicators.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2025 Jan;55(1):55-62. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2433242. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39688342 Review.
-
Imaging Findings and Toxicological Mechanisms of Nervous System Injury Caused by Diquat.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9272-9283. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04172-x. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38619744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
