Efficacy of acupuncture for hypertension in the elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38162142
- PMCID: PMC10756235
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1147135
Efficacy of acupuncture for hypertension in the elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Hypertension has now developed into a major public health problem worldwide. Under the existing antihypertensive drug treatment paradigm, problems such as decreasing drug resistance and increasing drug side effects can occur for elderly patients. Acupuncture, a core technique in the non-pharmacological treatment of Chinese medicine, plays an important role in the treatment of elevated blood pressure.
Objective: This study aimed to systematically evaluate the effect of acupuncture alone or in combination with antihypertensive drugs on the efficiency of reducing blood pressure and controlling blood pressure in elderly patients with hypertension.
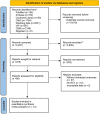
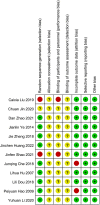
Methods: Articles of randomized controlled trials of acupuncture for hypertension in the elderly published before November 2022 were searched in 7 databases. The methodological quality of the literature was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool. The primary outcome was the efficiency rate of blood pressure reduction, and the secondary outcome was the change in blood pressure after treatment.
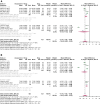
Results: This study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials with a total of 1,466 subjects. Among the primary outcome-efficiency rate, acupuncture-only treatment (RR = 1.11, 95% CI: 1.03-1.20, P < 0.01) and acupuncture combined with antihypertensive drug treatment (RR = 1.18, 95% CI: 1.06-1.31, P < 0.01) were significantly different compared with drugs-only treatment. Among the secondary outcomes, SBP (MD: -4.85, 95% CI: -10.39 to -0.69, P = 0.09) and DBP (MD: -1.45, 95% CI: -5.35 to 2.45, P = 0.47) show no significant difference between acupuncture-only treatment and drug-only treatment. Compared to drugs-only treatment, acupuncture plus drugs has more significant efficiency in lowering SBP (MD: -9.81, 95% CI: -13.56 to -6.06, P < 0.01) and DBP (MD: -7.04, 95% CI: -10.83 to -3.24, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: For elderly patients with hypertension, acupuncture-only treatment has the same efficiency and antihypertensive effect compared to drug therapy and acupuncture plus drugs outperforms drugs-only treatment. If the patients receive therapy with less frequency per week and longer duration, there will be a more obvious antihypertensive effect. Due to the methodological defects in the included study and the limited sample size of this paper, more well-designed randomized controlled trials are needed for verification.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42022376407, PROSPERO (CRD42022376407).
Keywords: acupuncture; elderly; hypertension; meta-analysis; systematic review.
© 2023 Wang, Li, Feng, Wang, Qin, Zhang, Sun, Wang, Cai, Han, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Acupuncture treatment vs. cognitive rehabilitation for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1035125. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1035125. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36846126 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture in Parkinson's disease with dysphagia.Front Neurol. 2023 May 26;14:1099012. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1099012. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37305760 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2023 Nov 16;14:1281485. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1281485. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38046594 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for insomnia symptoms in hypertensive patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1329132. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1329132. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38440112 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of acupuncture for disorders of consciousness in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 5;13:930546. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.930546. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36277925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ettig R, Unger O. The role of the kidney in the aetiologyof hypextension: renal transplantationshdies in rats. Trends Plant Sci. (1991) 12:243–5. 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90562-7 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

