Assessing the efficacy of machine learning algorithms for syncope classification: A systematic review
- PMID: 38162148
- PMCID: PMC10755776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102508
Assessing the efficacy of machine learning algorithms for syncope classification: A systematic review
Abstract
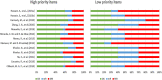
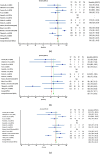
Syncope is a transient loss of consciousness with rapid onset. The aims of the study were to systematically evaluate available machine learning (ML) algorithm for supporting syncope diagnosis to determine their performance compared to existing point scoring protocols. We systematically searched IEEE Xplore, Web of Science, and Elsevier for English articles (Jan 2011 - Sep 2021) on individuals aged five and above, employing ML algorithms in syncope detection with Head-up titl table test (HUTT)-monitored hemodynamic parameters and reported metrics. Extracted data encompassed subject count, age range, syncope protocols, ML type, hemodynamic parameters, and performance metrics. Of the 6301 studies initially identified, 10 studies, involving 1205 participants aged 5 to 82 years, met the inclusion criteria, and formed the basis for it. Selected studies must use ML algorithms in syncope detection with hemodynamic parameters recorded throughout HUTT. The overall ML algorithm performance achieved a sensitivity of 88.8% (95% CI: 79.4-96.1%), specificity of 81.5% (95% CI: 69.8-92.8%) and accuracy of 85.8% (95% CI: 78.6-92.8%). Machine learning improves syncope diagnosis compared to traditional scoring, requiring fewer parameters. Future enhancements with larger databases are anticipated. Integrating ML can curb needless admissions, refine diagnostics, and enhance the quality of life for syncope patients.
Keywords: Classification; Machine learning; Methodology for conducting a systematic literature review; Syncope diagnosis; Systematic review.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Study of the efficiency of the head-up tilt test with nitroglycerin challenge in the diagnosis of vasovagal syncope.Rom J Intern Med. 2004;42(3):585-94. Rom J Intern Med. 2004. PMID: 16366132
-
Clinical Decision-Support Systems for Detection of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, Sepsis, and Septic Shock in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review.Methods Inf Med. 2019 Dec;58(S 02):e43-e57. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1695717. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Methods Inf Med. 2019. PMID: 31499571
-
The predictive effect of different machine learning algorithms for pressure injuries in hospitalized patients: A network meta-analyses.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 2;8(11):e11361. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11361. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36387440 Free PMC article.
-
Psychophysiological evaluation of patients with transient consciousness loss of uncertain origin.Kardiol Pol. 2018;76(3):566-573. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2017.0254. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Kardiol Pol. 2018. PMID: 29297196
-
Early Prediction of Sepsis in the ICU Using Machine Learning: A Systematic Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 28;8:607952. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.607952. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34124082 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Natural language processing systems for extracting information from electronic health records about activities of daily living. A systematic review.JAMIA Open. 2024 May 24;7(2):ooae044. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooae044. eCollection 2024 Jul. JAMIA Open. 2024. PMID: 38798774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances and Future Directions in Syncope Management: A Comprehensive Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 26;13(3):727. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030727. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brignole M., Moya A., De Lange F.J., Deharo J.C., Elliott P.M., Fanciulli A., et al. 2018 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope. Eur. Heart J. 2018;39(21):1883–1948. - PubMed
-
- Walsh K., Hoffmayer K., Hamdan M.H. Syncope: diagnosis and management. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2015;40(2):51–86. - PubMed
-
- Runser L.A., Gauer R.L., Houser A. Syncope: evaluation and differential diagnosis. Am. Fam. Physician. 2017;95(5):303–312. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

