Biogenic Zinc oxide nanoparticles from Celosia argentea: toward improved antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer activities
- PMID: 38162186
- PMCID: PMC10757369
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1283898
Biogenic Zinc oxide nanoparticles from Celosia argentea: toward improved antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer activities
Abstract
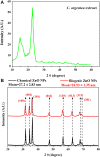
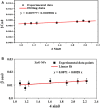
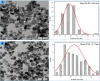
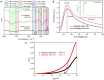
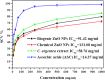
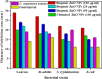
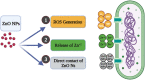
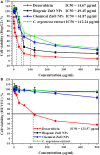
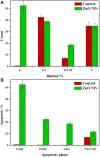
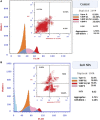
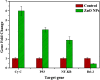
Biogenic Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized from Celosia argentea (C. argentea) plant extract. Structural analysis confirms the successful synthesis of biogenic zinc oxide NPs from C. argentea extract. The biogenic ZnO NPs have an average particle size of 21.55 ± 4.73 nm, a semispherical shape, and a specific surface area of about 50 m2/g. The biogenic ZnO NPs have a powerful radical scavenging activity (Ic50 = 91.24 mg/ml) comparable to ascorbic acid (ASC) as a standard (Ic50 = 14.37 mg/ml). The antibacterial efficacy was tested against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria using an agar disc diffusion method. Gram-positive strains with biogenic ZnO NPs have a greater bactericidal impact than gram-negative strains in a concentration-dependent manner. Anticancer activity against Liver hepatocellular cells (HepG2) and Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) was evaluated using a [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] (MTT) assay. The results reflect the concentration-dependent cytotoxic effect of biogenic ZnO NPs against HepG2 cells even at low concentrations (Ic50 = 49.45 μg/ml) compared with doxorubicin (Ic50 = 14.67 μg/ml) and C. argentea extract (Ic50 = 112.24 μg/ml). The cell cycle and gene expression were analyzed to determine the potential anticancer mechanism. The flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle revealed that biogenic ZnO NPs induce oxidative stress that activates the apoptotic genes NF-κB, CY-C, and P53, leading to cell death. The Celosia argentea improved the antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer activities of ZnO NPs without altering their structural properties. The effect of green synthesis on the bioactivity of biogenic ZnO NPs in vivo is recommended for future work.
Keywords: Celosia argentea; ZnO NPs; antibacterial; anticancer; antioxidant.
Copyright © 2023 Alghamdi, Al-Zahrani, Altarjami, Al Abdulmonem, Samir, Said, Shami, Mohamed and Ezzeldien.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Dec 20;14:87-100. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S186888. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30587987 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles synthesized from Tinospora Cordifolia induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer.Nanotheranostics. 2024 Mar 9;8(3):312-329. doi: 10.7150/ntno.84995. eCollection 2024. Nanotheranostics. 2024. PMID: 38577319 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of antibacterial and photocatalytic efficiency of green ZnO nanoparticles that synthesized with Celosia Cristata flower extract.Turk J Chem. 2021 Sep 1;46(1):59-85. doi: 10.3906/kim-2007-10. eCollection 2022. Turk J Chem. 2021. PMID: 38143892 Free PMC article.
-
Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism.Nanomicro Lett. 2015;7(3):219-242. doi: 10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Nanomicro Lett. 2015. PMID: 30464967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bactericidal and Virucidal Activities of Biogenic Metal-Based Nanoparticles: Advances and Perspectives.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 28;10(7):783. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070783. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytogenic-Mediated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using the Seed Extract of Citrullus lanatus and Its Integrated Potency against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 28;9(14):16832-16841. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01554. eCollection 2024 Apr 9. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38617622 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities of biogenic synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Mallotus philippinensis Mull. Arg.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 24;15(1):6541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85264-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39994261 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Promising Antibacterial Agent: Synthesis and Characterization.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 31;25(17):9500. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179500. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenic synthesis and physicochemical characterization of metal nanoparticles based on Calotropis procera as promising sustainable materials against skin cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):25154. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76422-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39448765 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-Formulations of Natural Antioxidants for the Treatment of Liver Cancer.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 19;14(8):1031. doi: 10.3390/biom14081031. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alharbi F. N., Abaker Z. M., Makawi S. Z. A. (2023). Phytochemical substances—mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPS). Inorganics 11 (8), 328. 10.3390/inorganics11080328 - DOI
-
- Al-Harbi L. M., Mohamed W. S., Ebnalwaled A. A., Said A. H., Ezzeldien M. (2023). The effect of synthesis conditions on the photokilling activity of TiO 2 nanostructures. Mater Res. Express 10 (1), 015004. 10.1088/2053-1591/acb121 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

