Glycosylation and methylation in the biosynthesis of isoflavonoids in Pueraria lobata
- PMID: 38162309
- PMCID: PMC10757850
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1330586
Glycosylation and methylation in the biosynthesis of isoflavonoids in Pueraria lobata
Abstract
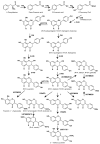
The pathway for forming isoflavonoid skeletal structure is primarily restricted to the Leguminosae family. Subsequent decorations on the compound backbone by tailoring enzymes would change their biological and medicinal properties. Pueraria lobata is a leguminous plant, and as a traditional Chinese medicine its roots have been ascribed a number of pharmacological activities. Glycosylation and methylation are the main modifying processes in isoflavonoid metabolism in P. lobata roots, resulting in the accumulation of unique glycosylated and methylated end isoflavonoid compounds. For instance, daidzein 8-C-glucoside (i.e., puerarin) and puerarin derivatives are produced only by the Pueraria genus. Puerarin has been established as a clinical drug for curing cardiovascular diseases. To better understand the characteristic isoflavonoid metabolism in P. lobata, this review attempts to summarize the research progress made with understanding the main glycosylation and methylation of isoflavonoids in P. lobata and their biosynthetic enzymes.
Keywords: biosynthesis; glycosylation; isoflavonoid; methylation; pueraria.
Copyright © 2023 Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of the C-glucosylation for puerarin biosynthesis in Pueraria lobata.Plant J. 2017 May;90(3):535-546. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13510. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28207970
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of roots, stems, and leaves of Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi: identification of genes involved in isoflavonoid biosynthesis.PeerJ. 2021 Feb 22;9:e10885. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10885. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33665027 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Transcription Factor Genes and Functional Characterization of PlMYB1 From Pueraria lobata.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 8;12:743518. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.743518. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34691120 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Methods of Puerarin Biotransformation.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016;16(17):1392-1402. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160505114456. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27145856 Review.
-
Protective effect of isoflavones and triterpenoid saponins from pueraria lobata on liver diseases: A review.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Dec 10;10(1):272-285. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2668. eCollection 2022 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 35035928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Analyses of Metabolome and Transcriptome Reveal Regulatory Network of Puerarin Biosynthesis in Pueraria montana var. lobata.Molecules. 2024 Nov 25;29(23):5556. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235556. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683717 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Novel Pueroside B Isomers and Other Bioactive Compounds from Pueraria lobata Roots: Structure Elucidation, α-Glucosidase, and α-Amylase Inhibition Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 4;25(17):9602. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179602. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273546 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the power of Pueraria lobata: a comprehensive exploration of its medicinal and edible potentials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 10;16:1578472. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578472. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40709088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Puerarin-A Promising Flavonoid: Biosynthesis, Extraction Methods, Analytical Techniques, and Biological Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5222. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105222. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akashi T., Sawada Y., Shimada N., Sakurai N., Aoki T., Ayabe S. (2003). cDNA cloning and biochemical characterization of S-adenosyl-L-methionine: 2,7,4’-trihydroxyisoflavanone 4’-O-methyltransferase, a critical enzyme of the legume isoflavonoid phytoalexin pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 44 (2), 103–112. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcg034 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

