Hemp-Based Sustainable Slippery Surfaces: Icephobic and Antithrombotic Properties
- PMID: 38162324
- PMCID: PMC10756499
- DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c06233
Hemp-Based Sustainable Slippery Surfaces: Icephobic and Antithrombotic Properties
Abstract
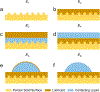
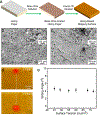
With the passage of the 2018 Farm Bill that removed hemp from the Controlled Substances Act altogether, production of hemp is experiencing a renaissance. Building on this revival and re-emergence of hemp, we designed and fabricated hemp-based sustainable and robust slippery surfaces by coating hemp paper with beeswax and subsequently infusing it with hemp oil. A wide variety of aqueous liquids and beverages easily slide on our hemp-based sustainable slippery surfaces, without leaving a trace. We also fabricated hemp-based sustainable slippery surfaces using different textured metals. Our hemp-based sustainable slippery metal surfaces display good icephobic and antithrombotic properties. With these attributes, we envision that our hemp-based sustainable slippery surfaces will pave the path to more safe, non-toxic, and biodegradable or recyclable slippery surfaces for applications in food packaging, anti-icing or de-icing coatings, and antithrombotic medical devices.
Keywords: antithrombotic property; hemp-based sustainable slippery surface; icephobicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gaustad G; Olivetti E; Kirchain R Toward Sustainable Material Usage: Evaluating the Importance of Market Motivated Agency in Modeling Material Flows. Environ. Sci. Technol 2011, 45, 4110–4117. - PubMed
-
- Miller SA Sustainable polymers: opportunities for the next decade. ACS Macro Lett 2013, 2, 550–554. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y; Romain C; Williams CK Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362. - PubMed
-
- Arroyo P; Tommelein ID; Ballard G Selecting globally sustainable materials: a case study using choosing by advantages. J. Constr. Eng 2016, 142, 501–5015.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
