The effectiveness and safety of palbociclib and ribociclib in stage IV HR+/HER-2 negative breast cancer: a nationwide real world comparative retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38162489
- PMCID: PMC10757634
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1203684
The effectiveness and safety of palbociclib and ribociclib in stage IV HR+/HER-2 negative breast cancer: a nationwide real world comparative retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Palbociclib and ribociclib are indicated in the first-line treatment of hormonal receptor-positive HER-2 negative (HR+/HER2- negative) advanced breast cancer. Although randomized-controlled trials (RCTs) proved their clinical efficacy, there are no observational studies yet to validate the clinical findings in the real-world. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate and compare the clinical effectiveness and safety profiles of palbociclib and ribociclib in Qatar.
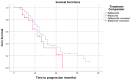
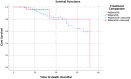
Materials and methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted on HR+/HER-2-negative stage-IV breast cancer patients receiving palbociclib or ribociclib in the state of Qatar. Clinical data were collected from the National Center for Cancer Care and Research (NCCCR) in Qatar using Cerner®. Primary outcomes were progression-free-survival (PFS) and overall-survival (OS) generated by Kaplan-Meier curves. Moreover, safety profiles of both two treatments were evaluated.
Results: The data from 108 patients were included in the final analysis. There was no statistically significant difference in PFS between the palbociclib and ribociclib groups; PFS was 17.85 versus 13.55 months, respectively(p> 0.05). Similarly, there was no statistically significant difference in OS between the two medications, 29.82 versus 31.72 months, respectively(p>0.05). Adverse events were similar between the two groups. Neutropenia was the most common side effect in the study population accounting for 59.3% of the patients.
Conclusions: Therefore, both treatments have similar efficacy and safety profiles. Further research on a larger-scale population and longer follow-up period is recommeneded.
Keywords: CDK4/6 cell cycle inhibitors; HR+/HER-2 negative; advanced breast cancer (ABC); cyclin-dependent-kinase 4/6 inhibitors; effectiveness & efficiency (E&E).
Copyright © 2023 Al-Ziftawi, Elazzazy, Alam, Shafie, Hamad, Bbujassoum and Mohamed Ibrahim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of CDK4/6 inhibitors combined with endocrine therapies for HR+/HER2-breast cancer: Systematic review and network meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 May 21;10(11):e31583. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31583. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38832268 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Ribociclib plus Letrozole Versus Palbociclib plus Letrozole and Letrozole Monotherapy in the First-Line Treatment of Postmenopausal Women with HR+/HER2- Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer: A U.S. Payer Perspective.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018 Jun;24(6):514-523. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.6.514. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29799329 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of ribociclib versus palbociclib in combination with an aromatase inhibitor as first-line treatment of postmenopausal women with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer: analysis based on final OS results of MONALEESA-2 and PALOMA-2.J Med Econ. 2023 Jan-Dec;26(1):357-365. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2023.2182051. J Med Econ. 2023. PMID: 36797664
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors for the management of advanced or metastatic breast cancer in women.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019 Aug 1;76(16):1183-1202. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxz121. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31369120 Review.
-
Pharmacoeconomic evaluations of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy for advanced hormone receptor-positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HER2-) breast cancer: a systematic review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Feb;10(4):233. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5110. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35280368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative overall survival of CDK4/6 inhibitors plus an aromatase inhibitor in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer in the US real-world setting.ESMO Open. 2025 Jan;10(1):104103. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.104103. Epub 2025 Jan 3. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 39754979 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative cost-effectiveness analysis of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the first-line treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: a Markov's model-based evaluation.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;14:1413676. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1413676. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39114308 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Real-World Studies.Target Oncol. 2025 Jan;20(1):71-88. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01118-0. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Target Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39656361
-
Single-cell analysis of matrisome-related genes in breast invasive carcinoma: new avenues for molecular subtyping and risk estimation.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1466762. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466762. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39493752 Free PMC article.
-
Schisandrin B targets CDK4/6 to suppress proliferation and enhance radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inducing cell cycle arrest.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 12;15(1):8452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92992-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer . Latest global cancer data: Cancer burden rises to 18.1 million new cases and 9.6 million cancer deaths in 2018. World Health Organization; (2018). Available at: https://www.who.int/cancer/PRGlobocanFinal.pdf?ua=1.
-
- World Health Organization . Cancer Report 2020- Global Profile (2020). Available at: https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&view=download&catego....
-
- Treating Breast Cancer . American Cancer Society. (2020). Available at: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/8581.00.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous