Ciprofloxacin and pegylated G-CSF combined therapy mitigates brain hemorrhage and mortality induced by ionizing irradiation
- PMID: 38162617
- PMCID: PMC10756649
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1268325
Ciprofloxacin and pegylated G-CSF combined therapy mitigates brain hemorrhage and mortality induced by ionizing irradiation
Abstract
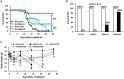
Introduction: Brain hemorrhage was found between 13 and 16 days after acute whole-body 9.5 Gy 60Co-γ irradiation (IR). This study tested countermeasures mitigating brain hemorrhage and increasing survival from IR. Previously, we found that pegylated G-CSF therapy (PEG) (i.e., Neulasta®, an FDA-approved drug) improved survival post-IR by 20-40%. This study investigated whether Ciprofloxacin (CIP) could enhance PEG-induced survival and whether IR-induced brain hemorrhage could be mitigated by PEG alone or combined with CIP.
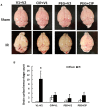
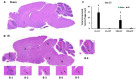
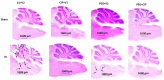
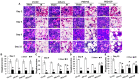
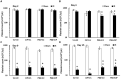
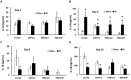
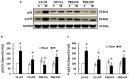
Methods: B6D2F1 female mice were exposed to 60Co-γ-radiation. CIP was fed to mice for 21 days. PEG was injected on days 1, 8, and 15. 30-day survival and weight loss were studied in mice treated with vehicles, CIP, PEG, or PEG + CIP. For the early time point study, blood and sternums on days 2, 4, 9, and 15 and brains on day 15 post-IR were collected. Platelet numbers, brain hemorrhage, and histopathology were analyzed. The cerebellum/pons/medulla oblongata were detected with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), p53, p16, interleukin-18 (IL-18), ICAM1, Claudin 2, ZO-1, and complement protein 3 (C3).
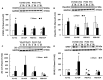
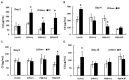
Results: CIP + PEG enhanced survival after IR by 85% vs. the 30% improvement by PEG alone. IR depleted platelets, which was mitigated by PEG or CIP + PEG. Brain hemorrhage, both surface and intracranial, was observed, whereas the sham mice displayed no hemorrhage. CIP or CIP + PEG significantly mitigated brain hemorrhage. IR reduced GFAP levels that were recovered by CIP or CIP + PEG, but not by PEG alone. IR increased IL-18 levels on day 4 only, which was inhibited by CIP alone, PEG alone, or PEG + CIP. IR increased C3 on day 4 and day 15 and that coincided with the occurrence of brain hemorrhage on day 15. IR increased phosphorylated p53 and p53 levels, which was mitigated by CIP, PEG or PEG + CIP. P16, Claudin 2, and ZO-1 were not altered; ICAM1 was increased.
Discussion: CIP + PEG enhanced survival post-IR more than PEG alone. The Concurrence of brain hemorrhage, C3 increases and p53 activation post-IR suggests their involvement in the IR-induced brain impairment. CIP + PEG effectively mitigated the brain lesions, suggesting effectiveness of CIP + PEG therapy for treating the IR-induced brain hemorrhage by recovering GFAP and platelets and reducing C3 and p53.
Keywords: Ciprofloxacin; G-CSF; ICAM1; glial fibrillary acidic protein; hemorrhage; mouse; platelet; radiation.
Copyright © 2023 Kiang, Cannon, Olson, Zhai, Woods, Xu, Lin, Li, Hull, Jiang and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Combined Therapy of Pegylated G-CSF with Ciprofloxacin Mitigates Damage Induced by Lethal Ionizing Radiation to the Bone Marrow, Spleen, and Ileum by Increasing AKT Activation but Decreasing IL-18, C3, and miR-34a.Radiat Res. 2025 May 1;203(5):341-356. doi: 10.1667/RADE-24-00266.1. Radiat Res. 2025. PMID: 40181563
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogen-reduced platelets for the prevention of bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Mar 28;(3):CD009072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009072.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 30;7:CD009072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009072.pub3. PMID: 23543569 Updated.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
Cited by
-
Effects of combined ciprofloxacin and Neulasta therapy on intestinal pathology and gut microbiota after high-dose irradiation in mice.Front Public Health. 2024 May 14;12:1365161. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1365161. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38807988 Free PMC article.
-
Diprovocim protects against the radiation-induced damage via the TLR2 signaling pathway.Mol Med. 2025 Apr 17;31(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01198-2. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40247162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iijima S. Pathology of atomic bomb casualties. Acta Pathol Jpn. (1982) 32:237–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

