One-month assessment of Th-cell axis related inflammatory cytokines, IL-17 and IL-22 and their role in alcohol-associated liver disease
- PMID: 38162671
- PMCID: PMC10755956
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1202267
One-month assessment of Th-cell axis related inflammatory cytokines, IL-17 and IL-22 and their role in alcohol-associated liver disease
Abstract
Introduction: Changes in the expression of cyto- and chemokines due to alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) have been reported to be both protective and pathogenic. This study examined plasma levels of two key cytokines, Il-17 and Il-22, which construct the proinflammatory vs. anti-inflammatory axes across the spectrum of alcohol use disorder (AUD) and ALD including alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH) to determine the underlying status of the inflammation.
Methods: Forty-two males and females aged 25-63 yrs. were grouped as healthy controls (HV[n=8]), AUD with no liver injury (AUDNLI [n=8]), AUD with liver injury (AUDLI [n=8]), non-severe alcohol-associated hepatitis (NSAH [n=9]), and severe alcohol-associated hepatitis (SAH [n=9]). Demographic, drinking, and clinical data were collected. Blood samples were collected at baseline (BL, all subjects) and during week 4 (W4, only patients) for IL-17 and IL-22; and statistically analyzed.
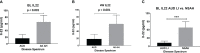
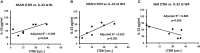
Results: IL-17 was highly elevated in the SAH group both at BL and post-SOC. LTDH and BL IL-22 in non-severe AH patients were associated significantly. LTDH significantly predicted W4 IL-22 levels, positively (increasing) in NSAH and inversely (lowering) in SAH patients. BL and W4 IL-22 levels were significantly higher (4-fold, p≤0.001) in all AH patients compared to all AUD patients (AUROC=0.988, p≤0.001). IL-22 showed significant affinity with AST, AST: ALT ratio, total bilirubin, INR, and PT both at BL and W4. IL-22 was inversely associated with IL-1β; and positively with TNF-α and IL-8 both at BL, and W4. BL IL-17 showed a positive correlation with MELD (p=0.017) in all AH patients. In SAH, > 2-fold W4 IL-17 level compared to BL showed significant within subjects' effects, p=0.006. In AUD patients without AH, the drop in IL-17 at W4 vs. BL showed a significant within subjects' effect, p=0.031.
Discussion: Drinking chronicity predicted opposite effects in IL-22 levels in NSAH (antiinflammatory) and SAH (pro-inflammatory) patients at post-SOC. BL IL-22 levels differentiated AH patients robustly from the AUD patients (with or without liver injury); and showed corresponding increases stepwise with the stages of ALD. IL-22 was closely associated with progression and injury markers of the liver; and response to the cytokines of pro-inflammatory nature. Pro-inflammatory indicator of IL-17 cell axis, IL-17 showed a strong positive association with MELD, a severity indicator of AH.
Keywords: IL-17; IL-22; alcohol use disorder; alcohol-associated hepatitis; audit.
Copyright © 2023 Sagaram, Frimodig, Jayanty, Hu, Royer, Bruner, Kong, Schwandt and Vatsalya.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Theragnostic Efficacy of K18 Response in Alcohol Use Disorder with Clinically Significant Fibrosis Using Gut-Liver Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 23;23(10):5852. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105852. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628661 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Hypomagnesemia in Alcoholic Hepatitis Patients and Its Association with Liver Injury and Severity Markers.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 19;12(8):2968. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082968. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109302 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with alcoholic hepatitis: relation to severity of liver disturbance.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000 Apr;24(4 Suppl):48S-54S. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000. PMID: 10803780
-
Current Status of Alcoholic Liver Disease in Japan and Therapeutic Strategy.Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2016 Aug;51(2):71-90. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 30462383 Review.
-
Relation of endotoxin, endotoxin binding proteins and macrophages to severe alcoholic liver injury and multiple organ failure.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Nov;29(11 Suppl):172S-179S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000189278.30237.e9. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16344605 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase ratio and mortality in critically ill patients with congestive heart failure.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 1;14(1):26317. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77141-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39487164 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in understanding the role of interleukins in pulmonary fibrosis (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2024 Nov 28;29(2):25. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12775. eCollection 2025 Feb. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39650776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cytokines in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Disease.Diseases. 2024 Mar 29;12(4):69. doi: 10.3390/diseases12040069. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 38667527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Electronic DSM-IV. Windows. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; (1994). p. 3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

