Soluble CD83 modulates human-monocyte-derived macrophages toward alternative phenotype, function, and metabolism
- PMID: 38162675
- PMCID: PMC10755915
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1293828
Soluble CD83 modulates human-monocyte-derived macrophages toward alternative phenotype, function, and metabolism
Abstract
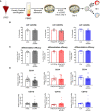
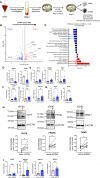
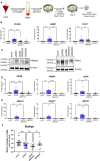
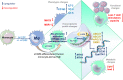
Alterations in macrophage (Mφ) polarization, function, and metabolic signature can foster development of chronic diseases, such as autoimmunity or fibrotic tissue remodeling. Thus, identification of novel therapeutic agents that modulate human Mφ biology is crucial for treatment of such conditions. Herein, we demonstrate that the soluble CD83 (sCD83) protein induces pro-resolving features in human monocyte-derived Mφ biology. We show that sCD83 strikingly increases the expression of inhibitory molecules including ILT-2 (immunoglobulin-like transcript 2), ILT-4, ILT-5, and CD163, whereas activation markers, such as MHC-II and MSR-1, were significantly downregulated. This goes along with a decreased capacity to stimulate alloreactive T cells in mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) assays. Bulk RNA sequencing and pathway analyses revealed that sCD83 downregulates pathways associated with pro-inflammatory, classically activated Mφ (CAM) differentiation including HIF-1A, IL-6, and cytokine storm, whereas pathways related to alternative Mφ activation and liver X receptor were significantly induced. By using the LXR pathway antagonist GSK2033, we show that transcription of specific genes (e.g., PPARG, ABCA1, ABCG1, CD36) induced by sCD83 is dependent on LXR activation. In summary, we herein reveal for the first time mechanistic insights into the modulation of human Mφ biology by sCD83, which is a further crucial preclinical study for the establishment of sCD83 as a new therapeutical agent to treat inflammatory conditions.
Keywords: LXR pathway; alternative activation; checkpoint molecule; human-monocyte-derived macrophages; soluble CD83.
Copyright © 2023 Peckert-Maier, Wild, Sprißler, Fuchs, Beck, Auger, Sinner, Strack, Mühl-Zürbes, Ramadan, Kunz, Krönke, Stich, Steinkasserer and Royzman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CD83 expressed by macrophages is an important immune checkpoint molecule for the resolution of inflammation.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 15;14:1085742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1085742. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875129 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-incubation of corneal donor tissue with sCD83 improves graft survival via the induction of alternatively activated macrophages and tolerogenic dendritic cells.Am J Transplant. 2022 Feb;22(2):438-454. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16824. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34467638
-
Nsp1α of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Strain BB0907 Impairs the Function of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells via the Release of Soluble CD83.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00366-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00366-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29793955 Free PMC article.
-
Tilting the Balance: Therapeutic Prospects of CD83 as a Checkpoint Molecule Controlling Resolution of Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 10;23(2):732. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020732. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Expanded Neuroimmunomodulation Axis: sCD83-Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-Kynurenine Pathway and Updates of Kynurenine Pathway in Neurologic Diseases.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 15;9:1363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01363. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29963055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced tolerogenic factor sCD83 in NMOSD and relapsing MOGAD: a potential new therapeutic pathway.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1620069. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620069. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40777014 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

