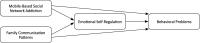The Relationship of Mobile-Based Social Network Addiction and Family Communication Patterns, with Behavioral Problems in Secondary School Students: The Mediating Role of Emotional Self-Regulation
- PMID: 38162808
- PMCID: PMC10755966
- DOI: 10.11621/pir.2023.0404
The Relationship of Mobile-Based Social Network Addiction and Family Communication Patterns, with Behavioral Problems in Secondary School Students: The Mediating Role of Emotional Self-Regulation
Abstract
Background: New technologies offer endless possibilities for students and schools, but as the use of smartphones increases, psychological and behavioral problems may also increase.
Objective: To investigate the relationship of mobile-based social network addiction and family communication patterns on the one hand, and behavioral problems in students on the other, with a focus on the mediating role of emotional self-regulation.
Design: This study used a quantitative approach and a cross-sectional design. The participants were 384 students (female/male: 226/168; mean age: 16 ± 1.98) in secondary high schools in Tehran in the academic year 2022-2023. The students were selected using convenience sampling. The data were collected online using the Revised Family Communication Pattern Scale (1994), Mobile-Based Social Network Addiction Questionnaire (2016), Child Behavior Checklist - Adolescent Version (2001), and the Affective Style Questionnaire (2010). The data were analyzed using structural equation modeling with SPSS-25 and AMOS-24 statistical software.
Results: The study showed that emotional self-regulation plays a mediating role in the relationship between mobile-based social network addiction and internalized and externalized behavioral problems (P ≤ .05). The indirect effect of conversation orientation on internalized and externalized behavioral problems mediated by emotional self-regulation was not significant, but the indirect effect of conformity orientation on internalized and externalized behavioral problems with the mediation of emotional self-regulation was significant (P ≤ .05).
Conclusion: Based on the findings, it is suggested that school officials and parents should develop emotional self-regulation and communication skills in students and parenting skills in their parents to prevent and reduce potential harm such as internet addiction and behavioral problems in students.
Keywords: behavioral problems; emotional self-regulation; family communication patterns; mobile-based social network addiction.
© Lomonosov Moscow State University, 2023© Russian Psychological Society, 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach, T.M. (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 and 1991 profile. University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Albursan, I.S., Al. Qudah, M.F., Al-Barashdi, H.S., Bakhiet, S. F., Darandari, E., Al-Asqah, S.S., ... & Albursan, H.I. (2022). Smartphone addiction among university students in light of the COVID-19 pandemic: Prevalence, relationship to academic procrastination, quality of life, gender and educational stage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10439. 10.3390/ijerph191610439 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Prentice-Hall, Inc.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources