Isolation and Molecular Detection of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from Clinically Pneumonic Pasteurellosis Cases of Bonga Sheep Breed and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Tests in Selected Areas of Southwest Ethiopian Peoples Regional State, Ethiopia
- PMID: 38162823
- PMCID: PMC10757770
- DOI: 10.2147/VMRR.S435932
Isolation and Molecular Detection of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from Clinically Pneumonic Pasteurellosis Cases of Bonga Sheep Breed and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Tests in Selected Areas of Southwest Ethiopian Peoples Regional State, Ethiopia
Abstract
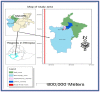
Background: Pneumonic pasteurellosis is a respiratory system disease of sheep caused by Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Bibersteinia trehalosi responsible for the low productivity and economic loss resulting from death and treatment costs. This study was conducted to isolate and molecularly detect causative agents and antibiotic susceptibility tests from a nasal swab sample of the Bonga sheep breed that was suspected to have pneumonic pasteurellosis in selected areas of Southwest Ethiopian Peoples Regional State.
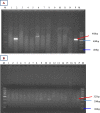
Methods: A cross-sectional study design was used along with purposive sampling of nasal swab samples from sheep that were brought to veterinary clinics during the study period. Bacterial isolation and phenotypic characterization were carried out using microbiological and biochemical tests that followed standard microbiological techniques. To molecularly confirm the isolates, PHSSA and KMT1, species-specific PCR primer genes were used. Using the disc diffusion method, molecularly confirmed isolates were subjected to an in vitro antibiotic susceptibility test.
Results: The 85 samples that were scrutinized had an overall isolation rate of 31.76%, whereas the isolates of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica had species compositions of 40.7% and 59.25%, respectively. Overall, 12.5% of the Mannheimia haemolytica and 18.18% of the Pasteurella multocida species were verified from phenotypical isolates using the species-specific PCR primer genes PHSSA and KMT1, respectively. An in vitro antibiotic susceptibility test was carried out on all four PCR-confirmed isolates for seven commonly used antibiotics used to treat ovine pasteurellosis in the study area. It was found that both bacterial species were resistant to chloramphenicol and penicillin G.
Conclusion: Using phenotypic and molecular diagnostic techniques, the results of our current inquiry revealed that Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica are the causative agents of ovine pneumonic pasteurellosis in the study area.
Keywords: Bonga sheep breed; Mannheimia haemolytica; Pasteurella multocida; antibiotics; isolation; pneumonia.
© 2023 Alemu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of serotypes of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida from pneumonic cases of sheep and goats and their antimicrobial sensitivity profiles in Borana and Arsi zones, Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 2;13(1):9008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36026-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37268660 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Identification of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica from Pneumonic Small Ruminants and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility in Haramaya District, Eastern Ethiopia.ScientificWorldJournal. 2024 Apr 16;2024:5605552. doi: 10.1155/2024/5605552. eCollection 2024. ScientificWorldJournal. 2024. PMID: 38655561 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Molecular Detection of Pasteurellosis from Pneumonic Sheep in Selected Areas of Amhara Region, Ethiopia: An Implication for Designing Effective Ovine Pasteurellosis Vaccine.Vet Med (Auckl). 2022 Apr 24;13:75-83. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S365267. eCollection 2022. Vet Med (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35497709 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and identification of caprine pasteurellosis in pneumonic goats in Bangladesh.J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023 Sep 30;10(3):538-544. doi: 10.5455/javar.2023.j707. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 2023. PMID: 37969786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mannheimia haemolytica and the pathogenesis of enzootic bronchopneumonia].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004 Mar-Apr;117(3-4):97-115. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004. PMID: 15046457 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The quadruplex fluorescent quantitative PCR method for the simultaneous detection of respiratory diseases in quail: Pasteurella multocida, Avibacterium paragallinarum, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Mycoplasma synoviae.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1605356. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1605356. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40661987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alemu and Merkel Sheep and Goat Production. Ethiopian sheep and goat productivity improvement Pro; 2008: 2–6.
-
- Alemneh T, Tewodros AA. Pasteurellosis in small ruminants: biochemical isolation, characterization and prevalence determination in relation to associated risk factors in Fogera Woreda, North-West Ethiopia. Advan Biological Res. 2015;9:330–337.
-
- Habashy HF, Fadel NG, El Shorbagy MM. Bacteriological and pathological studies on the causes of mortalities among sheep in sharkia-government farms. Egypt J Comparat Pathol Clin Path. 2009;22(1):130–146.
-
- Tadele K, Fikadu Z. Review on the pneumonic pasteurellosis of cattle. Acad J Animal Dis. 2015;4:177–184.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

