"It depends on the people!" - A qualitative analysis of contextual factors, prior to the implementation of digital health innovations for chronic condition management, in a German integrated care network
- PMID: 38162835
- PMCID: PMC10756073
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076231222100
"It depends on the people!" - A qualitative analysis of contextual factors, prior to the implementation of digital health innovations for chronic condition management, in a German integrated care network
Abstract
Objective: Integrated care and digital health technology interventions are promising approaches to coordinate services for people living with chronic conditions, across different care settings and providers. The EU-funded ADLIFE project intends to provide digitally integrated personalized care to improve and maintain patients' health with advanced chronic conditions. This study conducted a qualitative assessment of contextual factors prior to the implementation of the ADLIFE digital health platforms at the German pilot site. The results of the assessment are then used to derive recommendations for action for the subsequent implementation, and for evaluation of the other pilot sites.
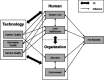
Methods: Qualitative interviews with healthcare professionals and IT experts were conducted at the German pilot site. The interviews followed a semi-structured interview guideline, based on the HOT-fit framework, focusing on organizational, technological, and human factors. All interviews were audio recorded, transcribed, and subsequently analysed following qualitative content analysis.
Results: The results of the 18 interviews show the interviewees' high openness and motivation to use new innovative digital solutions, as well as an apparent willingness of cooperation between different healthcare professionals. Challenges include limited technical infrastructure and large variability of software to record health data, lacking standards and interfaces.
Conclusions: Considering contextual factors on different levels is critical for the success of implementing innovations in healthcare and the transfer into other settings. In our study, the HOT-fit framework proved suitable for assessing contextual factors, when implementing IT innovations in healthcare. In a next step, the methodological approach will be transferred to the six other European pilot sites, participating in the project, for a cross-national assessment of contextual factors.
Keywords: IT-evaluation; Integrated care; digital health; digital healthcare technology; health information system; implementation assessment.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Effectiveness, Socio-Economic Impact and Implementation of a Digital Solution for Patients with Advanced Chronic Diseases: The ADLIFE Study Protocol.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 10;20(4):3152. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043152. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833849 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Design, implementation and usability analysis of patient empowerment in ADLIFE project via patient reported outcome measures and shared decision making.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Jun 28;24(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02588-y. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 38943152 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
New and emerging technology for adult social care - the example of home sensors with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023 Jun;11(9):1-64. doi: 10.3310/HRYW4281. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2023. PMID: 37470136
-
Healthcare stakeholders' perceptions and experiences of factors affecting the implementation of critical care telemedicine (CCT): qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 18;2(2):CD012876. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012876.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33599282 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Digital health intervention reconnects war-affected people living with HIV to healthcare: Ukraine case study.Oxf Open Digit Health. 2025 Jan 8;3:oqaf001. doi: 10.1093/oodh/oqaf001. eCollection 2025. Oxf Open Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40235841 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare Professionals Perspectives on Telemedicine for Patients With Chronic Diseases: A Qualitative Study.Nurs Health Sci. 2025 Jun;27(2):e70157. doi: 10.1111/nhs.70157. Nurs Health Sci. 2025. PMID: 40468555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Savarese G, Becher PM, Lund LH, et al. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res 2023; 118: 3272–3287. - PubMed
-
- Vogelmeier C, Buhl R, Burghuber O, et al. S2k-Leitlinie zur Diagnostik und Therapie von Patienten mit chronisch obstruktiver Bronchitis und Lungenemphysem (COPD), https://www.awmf.org/uploads/tx_szleitlinien/020-006l_S2k_COPD_chronisch... (2018, accessed 19 May 2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources