Diagnostic usefulness of deep learning methods for Helicobacter pylori infection using esophagogastroduodenoscopy images
- PMID: 38162866
- PMCID: PMC10757494
- DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.12995
Diagnostic usefulness of deep learning methods for Helicobacter pylori infection using esophagogastroduodenoscopy images
Abstract
Background and aims: We aimed to assess the diagnostic potential of deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) for detecting Helicobacter pylori infection in patients who underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy and Campylobacter-like organism tests.
Methods: We categorized a total of 13,071 images of various gastric sub-areas and employed five pretrained DCNN architectures: ResNet-101, Xception, Inception-v3, InceptionResnet-v2, and DenseNet-201. Additionally, we created an ensemble model by combining the output probabilities of the best models. We used images of different sub-areas of the stomach for training and evaluated the performance of our models. The diagnostic metrics assessed included area under the curve (AUC), specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value.
Results: When training included images from all sub-areas of the stomach, our ensemble model demonstrated the highest AUC (0.867), with specificity at 78.44%, accuracy at 80.28%, positive predictive value at 82.66%, and negative predictive value at 77.37%. Significant differences were observed in AUC between the ensemble model and the individual DCNN models. When training utilized images from each sub-area separately, the AUC values for the antrum, cardia and fundus, lower body greater curvature and lesser curvature, and upper body greater curvature and lesser curvature regions were 0.842, 0.826, 0.718, and 0.858, respectively, when the ensemble model was used.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that the DCNN model, designed for automated image analysis, holds promise for the evaluation and diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; artificial intelligence; deep learning.
© 2023 The Authors. JGH Open published by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures

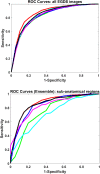
 , ensemble (RUC = 00867);
, ensemble (RUC = 00867);  , ResNet‐101 (AUC = 0.830);
, ResNet‐101 (AUC = 0.830);  , Xception (AUC = 0.8333);
, Xception (AUC = 0.8333);  , Inception‐v3 (AUC = 0.834);
, Inception‐v3 (AUC = 0.834);  , InceptionResnet‐v2 (AUC = 0.847);
, InceptionResnet‐v2 (AUC = 0.847);  , DenseNet‐201 (AUC = 0.846);
, DenseNet‐201 (AUC = 0.846);  , All (AUC = 0.867);
, All (AUC = 0.867);  , Angle (AUC = 0.753);
, Angle (AUC = 0.753);  , Antrum (AUC = 0.842);
, Antrum (AUC = 0.842);  , cardian and fundus (AUC = 0.826);
, cardian and fundus (AUC = 0.826);  , lower body GC and LC (AUC = 0.718);
, lower body GC and LC (AUC = 0.718);  , upper body GC and LC (AUC = 0.858).
, upper body GC and LC (AUC = 0.858).Similar articles
-
Advancing maxillofacial prosthodontics by using pre-trained convolutional neural networks: Image-based classification of the maxilla.J Prosthodont. 2024 Aug;33(7):645-654. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13853. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Prosthodont. 2024. PMID: 38566564
-
Ultrasonographic diagnosis of ovarian tumors through the deep convolutional neural network.Ginekol Pol. 2023 Oct 16. doi: 10.5603/gpl.94956. Online ahead of print. Ginekol Pol. 2023. PMID: 37842987
-
Application of artificial intelligence in endoscopic image analysis for the diagnosis of a gastric cancer pathogen-Helicobacter pylori infection.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 17;13(1):13380. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40179-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37592004 Free PMC article.
-
High Accuracy of Convolutional Neural Network for Evaluation of Helicobacter pylori Infection Based on Endoscopic Images: Preliminary Experience.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019 Dec;10(12):e00109. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000109. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31833862 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Critical Feeding Tube Malpositions on Radiographs Using Deep Learning.J Digit Imaging. 2019 Aug;32(4):651-655. doi: 10.1007/s10278-019-00229-9. J Digit Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31073816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hunt R, Xiao SD, Megraud F et al. Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. World gastroenterology organisation global guideline. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2011; 20: 299–304. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Ahn JY, Choi KD et al. Nationwide antibiotic resistance mapping of Helicobacter pylori in Korea: a prospective multicenter study. Helicobacter. 2019; 24: e12592. - PubMed
-
- Chey WD, Leontiadis GI, Howden CW, Moss SF. ACG clinical guideline: treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017; 112: 212–239. - PubMed
-
- Bang CS, Lee JJ, Baik GH. The most influential articles in Helicobacter pylori research: a bibliometric analysis. Helicobacter. 2019; 24: e12589. - PubMed
-
- Correa P. A human model of gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1988; 48: 3554–3560. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

