Incorporating Physical Activity Assessments and Behavior Change Techniques Into Geriatrics
- PMID: 38163022
- PMCID: PMC10757171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arrct.2023.100293
Incorporating Physical Activity Assessments and Behavior Change Techniques Into Geriatrics
Abstract
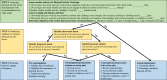
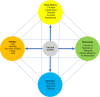
Ninety-one percent of adults 65 years and older do not perform the recommended levels of physical activity (PA), resulting in increased risk of disability, morbidity, and mortality. Despite knowing the benefits of PA and acknowledging the importance of assessing and addressing inadequate PA levels, 50%-75% of health care providers do not incorporate behavior change techniques into clinical practice. This clinical gap can be explained by a lack of knowledge or confidence in (1) assessing PA levels; (2) addressing inadequate PA levels; and (3) justifying the time needed to use these techniques in clinical practice. In this special communication, we address this gap by providing a 3-step theoretical-based clinical decision pathway that guides health care providers on how to identify older adults with inadequate PA levels, determine readiness to increase PA, and empower patents to develop an action plan that will increase their PA levels. We also provide a conceptual model that supports the use of techniques that assess and address inadequate PA by tying PA to the Age-Friendly Health System's 4Ms (ie, What Matters to the older adult, Mentation, Mobility, and Medications).
Keywords: Exercise; Primary prevention; Rehabilitation.
Figures
References
-
- Izquierdo M, Merchant RA, Morley JE, et al. International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines. J Nutr Health Aging. 2021;25:824–853. - PubMed
-
- Ding D, Lawson KD, Kolbe-Alexander TL, et al. The economic burden of physical inactivity: a global analysis of major non-communicable diseases. Lancet. 2016;388:1311–1324. - PubMed
-
- Lobelo F, Rohm Young D, Sallis R, et al. Routine assessment and promotion of physical activity in healthcare settings: a scientific statement from the. American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e495–e522. - PubMed
-
- Association of American Physical Therapy Association. Physical therapists’ role in prevention, wellness, fitness, health promotion, and management of disease and disability. 2019. Available at: https://www.apta.org/siteassets/pdfs/policies/pt-role-advocacy.pdf. Accessed August 8, 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous