Comprehensive analysis of m6A reader YTHDF2 prognosis, immune infiltration, and related regulatory networks in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38163150
- PMCID: PMC10756983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23204
Comprehensive analysis of m6A reader YTHDF2 prognosis, immune infiltration, and related regulatory networks in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification is the most prevalent internal modification pattern in eukaryotic mRNAs and plays critical roles in diverse physiological and pathological processes. However, the expression of m6A regulator YTHDF2, its prognostic value, its biological function, its correlation with tumor microenvironment (TME) immune infiltrates, and related regulatory networks in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain determined.
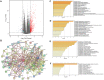
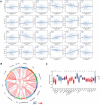
Methods: TCGA, GTEx, and GEO databases were used to investigate the expression profile of YTHDF2 in HCC. We performed differentially expressed genes (DEGs) analysis and constructed a PPI network to explore the biological processes of YTHDF2 in HCC. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox regression analysis were used to assess the prognostic value of YTHDF2 and then a clinical prognostic nomogram was constructed. Additionally, ssGSEA was performed to assess the correlation between YTHDF2 and immune infiltration levels. The TISIDB database was applied to explore the expression of YTHDF2 in immune and molecular subtypes of HCC. GSEA identifies the YTHDF2-related signaling pathways. Finally, we utilized miRNet and starBase database to construct regulatory networks for HCC based on lncRNA-miRNA and miRNA-YTHDF2 interactions.
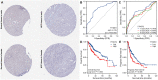
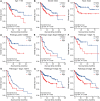
Results: YTHDF2 was significantly upregulated in HCC tumor tissues compared with the adjacent normal tissues. HCC patients in the high YTHDF2 expression group had poorer survival. Multivariate Cox analysis suggested that YTHDF2 may be a new independent prognostic indicator for HCC patients, with the prognostic nomogram exhibiting satisfactory results. YTHDF2 expression was significantly correlated with TME immune cell-infiltrating characteristics. Strong correlations were also shown in immune subtypes, molecular subtypes and immune checkpoints. Further analysis revealed that the combination of YTHDF2 expression and immune cell score was considerably associated with survival outcome in HCC patients. GESA analysis demonstrated that high YTHDF2 expression is associated with multiple biological processes and oncogenic pathways. Moreover, 14 possible regulatory networks were constructed, which are associated with HCC progression.
Conclusion: Our findings revealed that YTHDF2 may serve as a promising prognostic biomarker for HCC and may regulate the tumor immune microenvironment to provide effective therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Epitranscriptomics; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immune infiltration; Prognostic signature; m6A methylation.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine methylation-related genes YTHDF2, METTL3, and ZC3H13 predict the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1398. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5964. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660669 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of PD-L1 Expression, Immune Infiltrates, and m6A RNA Methylation Regulators in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 May 12;12:669750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669750. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054840 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Analyses of the Role of the Reader Protein of N 6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation, YTH Domain Family 2, in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Dec 2;7:577460. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.577460. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33344502 Free PMC article.
-
M6A-related lncRNAs predict clinical outcome and regulate the tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Aug 9;22(1):867. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09925-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35941582 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of N6-methyladenosine methylation-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Front Surg. 2023 Mar 3;10:1052100. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1052100. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36936652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding the Role of O-GlcNAcylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 25;14(8):908. doi: 10.3390/biom14080908. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting YTHDF2 with pH-responsive siRNA nanoparticles suppresses MYC m6A modification and restores antitumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 1;23(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03538-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40598231 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of PDZ domain-containing proteins is correlated with prognosis and immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;16(3):1176-1195. doi: 10.21037/jgo-2024-1018. Epub 2025 Jun 20. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40672094 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation of a novel CD8+ T cell-associated prognostic signature for predicting clinical outcomes and immunotherapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma via integrating single-cell RNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jun 20;15(1):235. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01092-z. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38900330 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Transplantation for Non-hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2025 Sep-Oct;15(5):102558. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2025.102558. Epub 2025 Mar 27. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40303874 Review.
References
-
- Visvanathan A., et al. Essential role of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in glioma stem-like cells maintenance and radioresistance. Oncogene. 2018;37:522–533. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

