Cytokinin: From autoclaved DNA to two-component signaling
- PMID: 38163638
- PMCID: PMC11062471
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koad327
Cytokinin: From autoclaved DNA to two-component signaling
Abstract
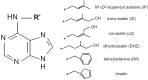
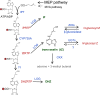
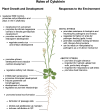
Since its first identification in the 1950s as a regulator of cell division, cytokinin has been linked to many physiological processes in plants, spanning growth and development and various responses to the environment. Studies from the last two and one-half decades have revealed the pathways underlying the biosynthesis and metabolism of cytokinin and have elucidated the mechanisms of its perception and signaling, which reflects an ancient signaling system evolved from two-component elements in bacteria. Mutants in the genes encoding elements involved in these processes have helped refine our understanding of cytokinin functions in plants. Further, recent advances have provided insight into the mechanisms of intracellular and long-distance cytokinin transport and the identification of several proteins that operate downstream of cytokinin signaling. Here, we review these processes through a historical lens, providing an overview of cytokinin metabolism, transport, signaling, and functions in higher plants.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

