Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptors in the regulation of anxiety reactions
- PMID: 38163664
- PMCID: PMC10758207
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2200642
Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptors in the regulation of anxiety reactions
Abstract
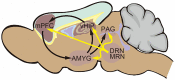
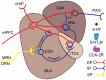
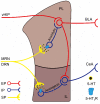
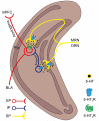
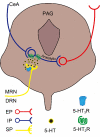
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) type 3 receptor (5-HT3R) is the only type of ligand-gated ion channel in the 5-HT receptor family. Through the high permeability of Na+, K+, and Ca2+ and activation of subsequent voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), 5-HT3R induces a rapid increase of neuronal excitability or the release of neurotransmitters from axon terminals in the central nervous system (CNS). 5-HT3Rs are widely expressed in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), amygdala (AMYG), hippocampus (HIP), periaqueductal gray (PAG), and other brain regions closely associated with anxiety reactions. They have a bidirectional regulatory effect on anxiety reactions by acting on different types of cells in different brain regions. 5-HT3Rs mediate the activation of the cholecystokinin (CCK) system in the AMYG, and the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) "disinhibition" mechanism in the prelimbic area of the mPFC promotes anxiety by the activation of GABAergic intermediate inhibitory neurons (IINs). In contrast, a 5-HT3R-induced GABA "disinhibition" mechanism in the infralimbic area of the mPFC and the ventral HIP produces anxiolytic effects. 5-HT2R-mediated regulation of anxiety reactions are also activated by 5-HT3R-activated 5-HT release in the HIP and PAG. This provides a theoretical basis for the treatment of anxiety disorders or the production of anxiolytic drugs by targeting 5-HT3Rs. However, given the circuit specific modulation of 5-HT3Rs on emotion, systemic use of 5-HT3R agonism or antagonism alone seems unlikely to remedy anxiety, which deeply hinders the current clinical application of 5-HT3R drugs. Therefore, the exploitation of circuit targeting methods or a combined drug strategy might be a useful developmental approach in the future.
5-羟色胺3受体(5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor,5-HT3R)是5-羟色胺受体家族中唯一的一类配体门控离子通道,通过对Na+、K+、Ca2+等离子的高通透性以及继发性电压门控Ca2+离子通道的激活从而诱发神经元兴奋性的快速上调或轴突末梢的神经递质释放。在中枢神经系统,5-HT3R广泛表达于内侧前额叶皮质、杏仁核、海马体和导水管周围灰质等与焦虑反应密切相关的脑区,通过对不同脑区不同类别细胞的作用,对焦虑反应产生双向调节效应。其中,5-HT3R在杏仁核通过激活胆囊收缩素系统促进焦虑;在内侧前额叶皮质的边缘下区通过激活γ-氨基丁酸能中间抑制性神经元的“去抑制”促进焦虑;在内侧前额叶皮质的边缘前区和腹侧海马则通过对γ-氨基丁酸能中间抑制性神经元的激活产生抗焦虑样作用。此外,在海马和导水管周围灰质,5-HT3R通过调节5-HT投射活动间接启动5-HT2R,从而参与焦虑反应调节。以上说明,仅通过全身性的激动或拮抗5-HT3R不太可能用于焦虑症治疗,这制约了当前5-HT3R药物的临床应用。因此,未来的研究可以探索针对5-HT3R涉及的环路进行靶向用药或联合药物的策略,以促进5-HT3R药物的临床应用。.
5-羟色胺3受体(5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor,5-HT3R)是5-羟色胺受体家族中唯一的一类配体门控离子通道,通过对Na +、K +、Ca 2+等离子的高通透性以及继发性电压门控Ca 2+离子通道的激活从而诱发神经元兴奋性的快速上调或轴突末梢的神经递质释放。在中枢神经系统,5-HT3R广泛表达于内侧前额叶皮质、杏仁核、海马体和导水管周围灰质等与焦虑反应密切相关的脑区,通过对不同脑区不同类别细胞的作用,对焦虑反应产生双向调节效应。其中,5-HT3R在杏仁核通过激活胆囊收缩素系统促进焦虑;在内侧前额叶皮质的边缘下区通过激活γ-氨基丁酸能中间抑制性神经元的“去抑制”促进焦虑;在内侧前额叶皮质的边缘前区和腹侧海马则通过对γ-氨基丁酸能中间抑制性神经元的激活产生抗焦虑样作用。此外,在海马和导水管周围灰质,5-HT3R通过调节5-HT投射活动间接启动5-HT2R,从而参与焦虑反应调节。以上说明,仅通过全身性的激动或拮抗5-HT3R不太可能用于焦虑症治疗,这制约了当前5-HT3R药物的临床应用。因此,未来的研究可以探索针对5-HT3R涉及的环路进行靶向用药或联合药物的策略,以促进5-HT3R药物的临床应用。
Keywords: 5-Hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor (5-HT 3 R); Amygdala; Anxiety; Hippocampus; Medial prefrontal cortex; Periaqueductal gray.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

