DTX2 promotes glioma development via regulation of HLTF
- PMID: 38163902
- PMCID: PMC10759338
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-023-00447-w
DTX2 promotes glioma development via regulation of HLTF
Abstract
Background: Human Deltex 2 (DTX2) is a ubiquitin E3 ligase that functions as an oncogene and has been shown to participate in many human cancers. However, the role of DTX2 in glioma progression has remained obscure. In this study, we explore the mechanism underlying the function of DTX2 in glioma progression.
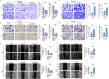
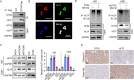
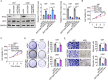
Methods: The associations between DTX2 expression and clinical characteristics of glioma were determined by bioinformatic analysis of data from The Cancer Genome Atlas and Human Protein Atlas. The expression of DTX2 in glioma tissues was detected using immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Lentivirus-mediated gene knockdown and overexpression were used to determine the effects of DTX2 and helicase-like transcription element (HLTF) on glioma cell proliferation and migration with CCK-8, cell colony formation, transwell, and wound healing assays; flow cytometry in vitro; and animal models in vivo. The interaction of the DTX2 and HLTF proteins was verified by immunoprecipitation assay and confocal microscopy.
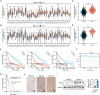
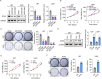
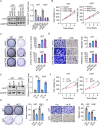
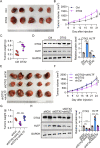
Results: DTX2 was highly expressed in glioma samples, and this was correlated with worse overall survival. Silencing of DTX2 suppressed glioma cell viability, colony formation, and migration and induced cell apoptosis. In vitro ubiquitination assays confirmed that DTX2 could downregulate HLTF protein levels by increasing ubiquitination of the HLTF protein. We also observed that HLTF inhibited proliferation and migration of glioma cells. Subcutaneous xenografts with DTX2-overexpressing U87 cells showed significantly increased tumor volumes and weights.
Conclusions: We have identified DTX2/HLTF as a new axis in the development of glioma that could serve as a prognostic or therapeutic marker.
Keywords: DTX2; Glioma; HLTF; Ubiquitination.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bromodomain containing 4 transcriptionally activated Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 2 contributes to glioma progression and predicts an unfavorable prognosis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(6):313. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-555. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35434025 Free PMC article.
-
[DTX2 overexpression promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the Notch2/Akt axis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Mar 20;43(3):340-348. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.03.02. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37087577 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
HLTF/SERPINE1 Axis Plays a Crucial Pro-Oncogenic Role in the Progression from Cervical Precancerous Lesions to Cervical Carcinoma in vitro.Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2025;90(2):108-119. doi: 10.1159/000540384. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2025. PMID: 39348822
-
The helicase-like transcription factor (HLTF) in cancer: loss of function or oncomorphic conversion of a tumor suppressor?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jan;73(1):129-47. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2060-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26472339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The helicase-like transcription factor and its implication in cancer progression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Feb;65(4):591-604. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7392-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18034322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[High expression of DTX2 promotes proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Apr 20;45(4):829-836. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.18. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40294933 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Therapeutic effects of paeonol on non‑small cell lung cancer cells via regulation of the MAPK pathway.Oncol Lett. 2024 Sep 24;28(6):560. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14693. eCollection 2024 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39372664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yonezawa T, Takahashi H, Hao Y, et al. The E3 ligase DTX2 inhibits RUNX1 function by binding its C terminus and prevents the growth of RUNX1-dependent leukemia cells. FEBS J. 2023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81201991/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202103021224400/the Basic Research Program of Shanxi Province
- 2021XM35/Key Medical Scientific Research Projects of Shanxi Province
- 2022RC07/Four "Batches" Innovation Project of Invigorating Medical through Science and Technology of Shanxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

