[Study on the Role and Mechanism of METTL3 Mediating the Up-regulation of m6A Modified Long Non-coding RNA THAP7-AS1 in Promoting the Occurrence of Lung Cancer]
- PMID: 38163978
- PMCID: PMC10767667
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.102.45
[Study on the Role and Mechanism of METTL3 Mediating the Up-regulation of m6A Modified Long Non-coding RNA THAP7-AS1 in Promoting the Occurrence of Lung Cancer]
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is a major threat to human health. The molecular mechanisms related to the occurrence and development of lung cancer are complex and poorly known. Exploring molecular markers related to the development of lung cancer is helpful to improve the effect of early diagnosis and treatment. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) THAP7-AS1 is known to be highly expressed in gastric cancer, but has been less studied in other cancers. The aim of the study is to explore the role and mechanism of methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) mediated up-regulation of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modified lncRNA THAP7-AS1 expression in promoting the development of lung cancer.
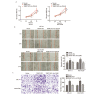
Methods: Samples of 120 lung cancer and corresponding paracancerous tissues were collected. LncRNA microarrays were used to analyze differentially expressed lncRNAs. THAP7-AS1 levels were detected in lung cancer, adjacent normal tissues and lung cancer cell lines by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The diagnostic value of THAP7-AS1 in lung cancer and the relationship between THAP7-AS1 expression and survival rate and clinicopathological parameters were analyzed. Bioinformatics analysis, methylated RNA immunoprecipitation (meRIP), RNA pull-down and RNA-immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay were used to investigate the molecular regulation mechanism of THAP7-AS1. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumorigenesis of SPC-A-1 and NCI-H1299 cells were determined by MTS, colony-formation, scratch, Transwell and xenotransplantation in vivo, respectively. Expression levels of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kenase B (PI3K/AKT) signal pathway related protein were detected by Western blot.
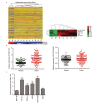
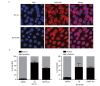
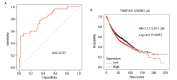
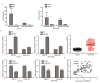
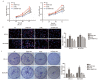
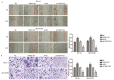
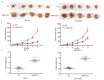
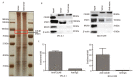
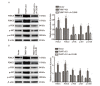
Results: Expression levels of THAP7-AS1 were higher in lung cancer tissues and cell lines (P<0.05). THAP7-AS1 has certain diagnostic value in lung cancer [area under the curve (AUC)=0.737], and its expression associated with overall survival rate, tumor size, tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage and lymph node metastasis (P<0.05). METTL3-mediated m6A modification enhanced THAP7-AS1 expression. The cell proliferation, migration, invasion and the volume and mass of transplanted tumor were all higher in the THAP7-AS1 group compared with the NC group and sh-NC group of SPC-A-1 and NCI-H1299 cells, while the cell proliferation, migration and invasion were lower in the sh-THAP7-AS1 group (P<0.05). THAP7-AS1 binds specifically to Cullin 4B (CUL4B). The cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and expression levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA), phosphoinositide-3 kinase, catalytic subunit delta (PIK3CD), phospho-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (p-PI3K), phospho-protein kinase B (p-AKT) and phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin (p-mTOR) were higher in the THAP7-AS1 group compared with the Vector group of SPC-A-1 and NCI-H1299 cells (P<0.05).
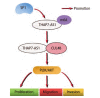
Conclusions: LncRNA THAP7-AS1 is stably expressed through m6A modification mediated by METTL3, and combines with CUL4B to activate PI3K/AKT signal pathway, which promotes the occurrence and development of lung cancer.
【中文题目:METTL3介导m6A修饰长链非编码RNA THAP7-AS1表达上调促进肺癌发生的作用及机制研究】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 肺癌是对人类健康的一大威胁,有关肺癌发生发展的分子机制复杂且知之尚少,探索与肺癌发展相关的分子标志物有利于提高早期诊断和治疗的效果。长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA , lncRNA)THAP7-AS1已知在胃癌中高表达,但在其他癌症中研究较少。本研究旨在探究甲基转移酶样3(methyltransferase-like 3, METTL3)介导N6-甲基腺苷(N6-methyladenosine, m6A)修饰lncRNA THAP7-AS1表达上调促进肺癌发生的作用及机制。方法 收集120例肺癌与对应癌旁组织样本,lncRNA微阵列分析差异表达的lncRNA,实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, qRT-PCR)检测肺癌、癌旁组织、肺癌细胞系THAP7-AS1表达,分析THAP7-AS1对肺癌的诊断价值以及其表达水平与肺癌患者生存率、临床病理特征的关系。通过生物信息学分析、甲基化RNA免疫共沉淀(methylated RNA immunoprecipitation, meRIP)、RNA pull-down实验、RIP实验探究THAP7-AS1的分子调节机制;通过MTS、克隆形成、划痕、Transwell、体内异种移植实验测定各组SPC-A-1、NCI-H1299细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭、成瘤能力,Western blot检测磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kenase B, PI3K/AKT)信号通路蛋白表达。结果 肺癌组织、细胞系THAP7-AS1表达升高(P<0.05),对肺癌具有一定的诊断价值[曲线下面积(area under the curve, AUC)=0.737],其表达水平与患者总生存率、肿瘤大小、肿瘤原发灶-淋巴结-转移(tumor-node-metastasis, TNM)分期、淋巴结转移相关(P<0.05)。METTL3介导的m6A修饰能够增强THAP7-AS1表达。与SPC-A-1、NCI-H1299细胞NC组、sh-NC组相比,THAP7-AS1组增殖、迁移、侵袭能力提高(P<0.05),移植瘤体积、质量增大(P<0.05),sh-THAP7-AS1组增殖、迁移、侵袭能力下降(P<0.05)。THAP7-AS1与Cullin蛋白4B(Cullin 4B, CUL4B)存在特异结合。与SPC-A-1、NCI-H1299细胞Vector组相比,THAP7-AS1组增殖、迁移、侵袭能力、磷脂酰肌醇-4,5-二磷酸3-激酶催化亚基α(phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha, PI3KCA)、磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶催化亚基δ(phosphoinositide-3 kinase-catalytic subunit delta, PI3KCD)、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phospho-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p-PI3K)、磷酸蛋白激酶B(phospho-protein kinase B, p-AKT)、磷酸哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(phospho-mammalian target of rapamycin, p-mTOR)表达水平升高(P<0.05)。结论 LncRNA THAP7-AS1通过METTL3介导的m6A修饰稳定表达,与CUL4B结合激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肺癌发生发展。 】 【中文关键词:甲基转移酶样3;N6-甲基腺苷;长链非编码RNA THAP7-AS1;肺肿瘤;增殖】.
Keywords: Long non-coding RNA THAP7-AS1; Lung neoplasms; Methyltransferase-like 3; N6-methyladenosine; Proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
lncRNA THAP7-AS1, transcriptionally activated by SP1 and post-transcriptionally stabilized by METTL3-mediated m6A modification, exerts oncogenic properties by improving CUL4B entry into the nucleus.Cell Death Differ. 2022 Mar;29(3):627-641. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00879-9. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Cell Death Differ. 2022. PMID: 34608273 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Represses Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Through Mediating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling by miR-342-3p/CUL4B Axis in Prostate Cancer.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Nov;35(9):661-672. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2019.3123. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 32275162
-
METTL3-mediated m6A modification of lnc RNA RHPN1-AS1 enhances cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by activating PI3K/AKT pathway.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Dec;36(12):e24761. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24761. Epub 2022 Nov 6. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 36336887 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the role of FOXD2-AS1 in human disorders.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Feb;254:155101. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155101. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38211387 Review.
-
Interplay between lncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the progression of digestive system neoplasms (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jan;55(1):15. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5456. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39513614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

