MicroRNA-145 Gene Modification Enhances the Retention of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells within Corpus Cavernosum by Targeting Krüppel-Like Factor 4
- PMID: 38164035
- PMCID: PMC11216959
- DOI: 10.5534/wjmh.230149
MicroRNA-145 Gene Modification Enhances the Retention of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells within Corpus Cavernosum by Targeting Krüppel-Like Factor 4
Abstract
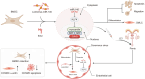
Purpose: The poor retention and ambiguous differentiation of stem cells (SCs) within corpus cavernosum (CC) limit the cell application in erectile dysfunction (ED). Herein, the effects and mechanism of microRNA-145 (miR-145) gene modification on modulating the traits and fate of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) were investigated.
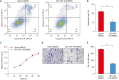
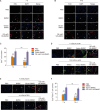
Materials and methods: The effects of miR-145 on cell apoptosis, proliferation, migration, and differentiation were determined by flow cytometry, cell counting kit-8, transwell assays and myogenic induction. Then, the age-related ED rats were recruited to four groups including phosphate buffer saline, BMSC, vector-BMSC, overexpressed-miR-145-BMSC groups. After cell transplantation, the CC were harvested and prepared to demonstrate the retention and differentiation of BMSCs by immunofluorescent staining. Then, the target of miR-145 was verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical. After that, APTO-253, as an inducer of Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), was introduced for rescue experiments in corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells (CCSMCs) under the co-culture system.
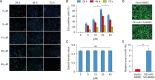
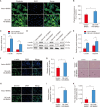
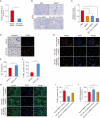
Results: In vitro, miR-145 inhibited the migration and apoptosis of BMSCs and promoted the differentiation of BMSCs into smooth muscle-like cells with stronger contractility. In vivo, the amount of 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU)+cells within CC was significantly enhanced and maintained in the miR-145 gene modified BMSC group. The EdU/CD31 co-staning was detected, however, no co-staining of EdU/α-actin was observed. Furthermore, miR-145, which secreted from the gene modified BMSCs, dampened the expression of KLF4. However, the effects of miR-145 on CCSMCs could be rescued by APTO-253.
Conclusions: Overall, miR-145 modification prolongs the retention of the transplanted BMSCs within the CC, and this effect might be attributed to the modulation of the miR-145/KLF4 axis. Consequently, our findings offer a promising and innovative strategy to enhance the local stem cell-based treatments.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cell differentiation; Erectile dysfunction; MicroRNAs; Stem cells.
Copyright © 2024 Korean Society for Sexual Medicine and Andrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-145 engineered bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviated erectile dysfunction in aged rats.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1509-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31852516 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(19):11512-11523. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15766. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32871042 Free PMC article.
-
d-Galactose induces the senescence and phenotype switch of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells.J Cell Physiol. 2024 Jan;239(1):124-134. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31150. Epub 2023 Nov 9. J Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37942832
-
miR-145 Regulates Diabetes-Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Induced Neurorestorative Effects in Diabetes Stroke Rats.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Dec;5(12):1656-1667. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0349. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27460851 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-21-5p downregulates PDCD4 and ameliorates erectile dysfunction in a rat model of diabetes mellitus.FASEB J. 2020 Oct;34(10):13345-13360. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000102RR. Epub 2020 Aug 17. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32808325
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs and hypospadias: A systematic review.Med Int (Lond). 2024 Nov 18;5(1):7. doi: 10.3892/mi.2024.206. eCollection 2025 Jan-Feb. Med Int (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39624466 Free PMC article.
-
miR-145-enriched BMSCs-derived exosomes ameliorate neurogenic erectile dysfunction in aged rats via TGFBR2 inhibition.Regen Ther. 2025 Apr 23;29:455-465. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.04.004. eCollection 2025 Jun. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 40308644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vakalopoulos I, Memmos D, Mykoniatis I, Toutziaris C, Dimitriadis G. Stem cell therapy in erectile dysfunction: science fiction or realistic treatment option? Hormones (Athens) 2018;17:315–320. - PubMed
-
- Gur S, Abdel-Mageed AB, Sikka SC, Hellstrom WJG. Advances in stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18:1137–1150. - PubMed
-
- Lin H, Dhanani N, Tseng H, Souza GR, Wang G, Cao Y, et al. Nanoparticle improved stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Urol. 2016;195:788–795. - PubMed
-
- Condorelli RA, Calogero AE, Vicari E, Favilla V, Morgia G, Cimino S, et al. Vascular regenerative therapies for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: current approaches. Andrology. 2013;1:533–540. - PubMed

