Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 38164178
- PMCID: PMC10750272
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.86305
Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia
Abstract
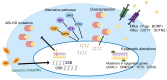
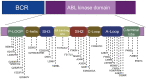
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a malignant clonal disease involving hematopoietic stem cells that is characterized by myeloid cell proliferation in bone marrow and peripheral blood, and the presence of the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome with BCR-ABL fusion gene. Treatment of CML has dramatically improved since the advent of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). However, there are a small subset of CML patients who develop resistance to TKI. Mutations in the ABL kinase domain (KD) are currently recognized as the leading cause of TKI resistance in CML. In this review, we discuss the concept of resistance and summarize recent advances exploring the mechanisms underlying CML resistance. Overcoming TKI resistance appears to be the most successful approach to reduce the burden of leukemia and enhance cures for CML. Advances in new strategies to combat drug resistance may rapidly change the management of TKI-resistant CML and expand the prospects for available therapies.
Keywords: ABL mutation; TKI Resistance; chronic myeloid leukemia; mechanism.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Jabbour E, Kantarjian H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2022 update on diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring. Am J Hematol. 2022;97:1236–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous