Comparison between 18F-FDG PET/CT and diffusion-weighted imaging in detection of invasive ductal breast carcinoma
- PMID: 38164229
- PMCID: PMC10757063
- DOI: 10.22038/AOJNMB.2023.70534.1493
Comparison between 18F-FDG PET/CT and diffusion-weighted imaging in detection of invasive ductal breast carcinoma
Abstract
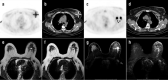
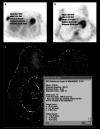
Objectives: Breast carcinoma is the most common type of cancer in females. This study aims to compare fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) uptake pattern and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value for the detection of the primary tumour and axillary metastases of invasive ductal breast carcinoma.
Methods: This study included 40 breast carcinoma lesions taken from 39 patients. After staging by positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT) and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), breast surgery with axillary lymph node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy was performed.
Results: Primary lesion detection rate for PET/CT and diffusion-weighted MRI was high with 39 of 40 lesions (97.5%). The sensitivity and specificity for the detection of metastatic lymph nodes in axilla were 40.9%, 88.9%, with 18F-FDG PET/CT scans and 40.9%, 83.3%, for dw-MRI, respectively. No significant correlation was detected between ADC and SUVmax or SUVmax ratios. Estrogen receptor (p=0.007) and progesterone receptor (p=0.036) positive patients had lower ADC values. Tumour SUVmax was lower in T1 than T2 tumour size (p=0.027) and progesterone receptor-positive patients (p=0.029). Tumour/background SUVmax was lower in progesterone receptor-positive patients (p=0.004). Tumour/liver SUVmax was higher in grade III patients (p=0.035) and progesterone receptor negative status (p=0.043).
Conclusions: This study confirmed the high detection rate of breast carcinoma in both modalities. They have same sensitivity for the detection of axillary lymph node metastases, whereas the PET/CT scan had higher specificity. Furthermore, ADC, SUVmax and SUVmax ratios showed some statistical significance among the patient groups according to different pathological parameters.
Keywords: Apparent diffusion coefficient Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; Breast carcinoma; Positron emission tomography; Standardized maximal uptake.
© 2024 mums.ac.ir All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
-
- Rim A, Chellman-Jeffers M. Trends in breast cancer screening and diagnosis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75:2–9. - PubMed
-
- Van Goethem M, Schelfout K, Kersschot E, Colpaert C, Verslegers I, Biltijes W, et al. MR mammography is useful in the preoperative locoregional staging of breast carcinomas with extensive intraductal component. Eur J Radiol. 2007;62(2):273–82. - PubMed
-
- Biglia N, Mariani L, Sgro L, Mininanni P, Moggio G, Sismondi P. Increased incidence of lobular breast cancer in women treated with hormone replacement therapy: implications for diagnosis, surgical and medical treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14(3):549–67. - PubMed
-
- Moon M, Cornfeld D, Weinreb J. Dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009;17(2):351–362. - PubMed
-
- Tamaki Y, Akashi-Tanaka S, Ishida T, Uematsu T, Sawai Y, Kusama M, et al. 3D imaging of intraductal spread of breast cancer and its clinical application for navigation surgery. Breast Cancer. 2002;9(4):289–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
