Periprostatic Adipose Tissue: A New Perspective for Diagnosing and Treating Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 38164282
- PMCID: PMC10751678
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.89750
Periprostatic Adipose Tissue: A New Perspective for Diagnosing and Treating Prostate Cancer
Abstract
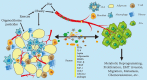
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common tumor of the male genitourinary system. It will eventually progress to fatal metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, for which treatment options are limited. Adipose tissues are distributed in various parts of the body. They have different morphological structures and functional characteristics and are associated with the development of various tumors. Periprostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) is the closest white visceral adipose tissue to the prostate and is part of the PCa tumor microenvironment. Studies have shown that PPAT is involved in PCa development, progression, invasion, and metastasis through the secretion of multiple active molecules. Factors such as obesity, diet, exercise, and organochlorine pesticides can affect the development of PCa indirectly or directly through PPAT. Based on the mechanism of PPAT's involvement in regulating PCa, this review summarized various diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for PCa with potential applications to assess the progression of patients' disease and improve clinical outcomes.
Keywords: and treatment; diagnosis; inflammation; lipids; periprostatic adipose tissue; prostate cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Sandhu S, Moore CM, Chiong E, Beltran H, Bristow RG, Williams SG. Prostate cancer. Lancet. 2021;398:1075–1090. - PubMed
-
- Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, De Santis M, Gross T. et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II: Treatment of Relapsing, Metastatic, and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol. 2017;71:630–642. - PubMed
-
- Sartor O, de Bono JS. Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:645–657. - PubMed
-
- de Bono JS, Oudard S, Ozguroglu M, Hansen S, Machiels JP, Kocak I. et al. Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel treatment: a randomised open-label trial. Lancet. 2010;376:1147–1154. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

