A Randomized Controlled Comparative Study of the Three Over-Bed Techniques for Positioning and Repositioning the Lithotomy Position While Using Stirrups
- PMID: 38164462
- PMCID: PMC10758315
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S435570
A Randomized Controlled Comparative Study of the Three Over-Bed Techniques for Positioning and Repositioning the Lithotomy Position While Using Stirrups
Abstract
Objective: In this study, the clinical application and efficacy of three different methods for placing and repositioning patients in the lithotomy position over the bed using stirrups were evaluated.
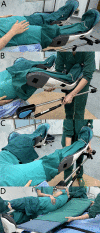
Methods: A total of 240 surgical patients who underwent surgery in Chongqing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital between July and November 2022 were selected as study participants. Using envelopes, they were randomly divided into three groups of 80 cases each using a randomization method. The groups included the traditional over-bed method, the postural trolley-assisted over-bed method, and the direct over-bed method. Using the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test, analysis of variance, and multiple linear regression equations, the placement time, over-bed repositioning time, and total time of the three methods for placing and repositioning in the lithotomy position supported by stirrups were analyzed statistically. In addition, we investigated and examined the satisfaction of nurses and doctors with the aforementioned techniques.
Results: The placement time, repositioning time, and total time were significantly higher for the traditional over-bed method than for the postural trolley-assisted over-bed method and the direct over-bed method (both P < 0.01). However, there was no statistically significant difference between the postural trolley-assisted over-bed method and the direct over-bed method (P > 0.05). Nurses and doctors reported significantly higher satisfaction with the postural trolley-assisted over-bed method and the direct over-bed method compared to the traditional over-bed method (both P < 0.01). In addition, nurses were more satisfied with the direct over-bed method than the postural trolley-assisted over-bed method (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The results of this study demonstrate that the direct over-bed method is preferred for positioning and repositioning patients in the lithotomy position with the support of stirrups.
Keywords: lithotomy position; position placement; postural trolley; repositioning over bed; stirrup.
© 2023 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any financial disclosure or conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preliminary comparative study of lower extremity pressure measurements under the conditions using former models and new lithotomy stirrups in rectal cancer surgery.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Apr 3;22(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03352-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38566192 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Lower Extremity Neuropathy With Boot Stirrups Compared With Candy Cane Stirrups.Obstet Gynecol. 2021 May 1;137(5):916-923. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004353. Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33831927 Free PMC article.
-
Stirrups to minimize complications of prolonged dorsal lithotomy positioning.J Urol. 1988 Feb;139(2):326-7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)42399-8. J Urol. 1988. PMID: 3339732
-
Intraoperative peripheral nerve injury related to lithotomy positioning with steep Trendelenburg in patients undergoing robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery - A systematic review.J Adv Nurs. 2020 Feb;76(2):490-503. doi: 10.1111/jan.14271. Epub 2019 Dec 2. J Adv Nurs. 2020. PMID: 31736124
-
Prone Compared With Lithotomy for Abdominoperineal Resection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Surg Res. 2019 Nov;243:469-480. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31377486
Cited by
-
Advanced Management of Complex Transplant Lithiasis: Low Lithotomy and Boot Stirrups Technique.Am J Case Rep. 2025 Jan 1;26:e946224. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.946224. Am J Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39741401 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

