Detection of heart rate using smartphone gyroscope data: a scoping review
- PMID: 38164464
- PMCID: PMC10757953
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1329290
Detection of heart rate using smartphone gyroscope data: a scoping review
Abstract
Heart rate (HR) is closely related to heart rhythm patterns, and its irregularity can imply serious health problems. Therefore, HR is used in the diagnosis of many health conditions. Traditionally, HR has been measured through an electrocardiograph (ECG), which is subject to several practical limitations when applied in everyday settings. In recent years, the emergence of smartphones and microelectromechanical systems has allowed innovative solutions for conveniently measuring HR, such as smartphone ECG, smartphone photoplethysmography (PPG), and seismocardiography (SCG). However, these measurements generally rely on external sensor hardware or are highly susceptible to inaccuracies due to the presence of significant levels of motion artifact. Data from gyrocardiography (GCG), however, while largely overlooked for this application, has the potential to overcome the limitations of other forms of measurements. For this scoping review, we performed a literature search on HR measurement using smartphone gyroscope data. In this review, from among the 114 articles that we identified, we include seven relevant articles from the last decade (December 2012 to January 2023) for further analysis of their respective methods for data collection, signal pre-processing, and HR estimation. The seven selected articles' sample sizes varied from 11 to 435 participants. Two articles used a sample size of less than 40, and three articles used a sample size of 300 or more. We provide elaborations about the algorithms used in the studies and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these methods. Across the articles, we noticed an inconsistency in the algorithms used and a lack of established standardization for performance evaluation for HR estimation using smartphone GCG data. Among the seven articles included, five did not perform any performance evaluation, while the other two used different reference signals (HR and PPG respectively) and metrics for accuracy evaluation. We conclude the review with a discussion of challenges and future directions for the application of GCG technology.
Keywords: GCG technology; digital health; heart rate monitor; mobile health; remote monitoring; seismocardiography; smart healthcare; smartphone application.
© 2023 Wu, Elgendi, Fletcher, Bomberg, Eichenberger, Guan and Menon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
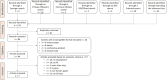
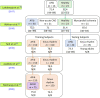

Similar articles
-
Accuracy of the Instantaneous Breathing and Heart Rates Estimated by Smartphone Inertial Units.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;25(4):1094. doi: 10.3390/s25041094. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006324 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing smartphone gyrocardiography for heart rate monitoring: overcoming clinical validation hurdles.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 25;10:1237043. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1237043. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37692045 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac monitoring of dogs via smartphone mechanocardiography: a feasibility study.Biomed Eng Online. 2019 Apr 23;18(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12938-019-0667-9. Biomed Eng Online. 2019. PMID: 31014339 Free PMC article.
-
Validity of resting heart rate derived from contact-based smartphone photoplethysmography compared with electrocardiography: a scoping review and checklist for optimal acquisition and reporting.Front Digit Health. 2024 Feb 29;6:1326511. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2024.1326511. eCollection 2024. Front Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38486919 Free PMC article.
-
Gyrocardiography: A Review of the Definition, History, Waveform Description, and Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 22;20(22):6675. doi: 10.3390/s20226675. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33266401 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accuracy of the Instantaneous Breathing and Heart Rates Estimated by Smartphone Inertial Units.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;25(4):1094. doi: 10.3390/s25041094. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006324 Free PMC article.
-
MSCardio seismocardiography dataset: Initial insights from remote monitoring of cardiovascular-induced chest vibrations via smartphones.Data Brief. 2025 Jul 17;61:111889. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2025.111889. eCollection 2025 Aug. Data Brief. 2025. PMID: 40792294 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone-Derived Seismocardiography: Robust Approach for Accurate Cardiac Energy Assessment in Patients with Various Cardiovascular Conditions.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;24(7):2139. doi: 10.3390/s24072139. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610349 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

