Fucoidan alleviated autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice by regulating pancreatic autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR1/TFEB pathway
- PMID: 38164477
- PMCID: PMC10722478
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68739.14981
Fucoidan alleviated autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice by regulating pancreatic autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR1/TFEB pathway
Abstract
Objectives: The present study investigated the effect and its underlying mechanisms of fucoidan on Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice.
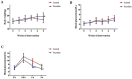
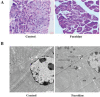
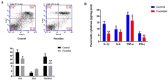
Materials and methods: Twenty 7-week-old NOD mice were used in this study, and randomly divided into two groups (10 mice in each group): the control group and the fucoidan treatment group (600 mg/kg. body weight). The weight gain, glucose tolerance, and fasting blood glucose level in NOD mice were detected to assess the development of diabetes. The intervention lasted for 5 weeks. The proportions of Th1/Th2 cells from spleen tissues were tested to determine the anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan. Western blot was performed to investigate the expression levels of apoptotic markers and autophagic markers. Apoptotic cell staining was visualized through TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL).
Results: The results suggested that fucoidan ameliorated T1DM, as evidenced by increased body weight and improved glycemic control of NOD mice. Fucoidan down-regulated the Th1/Th2 cells ratio and decreased Th1 type pro-inflammatory cytokines' level. Fucoidan enhanced the mitochondrial autophagy level of pancreatic cells and increased the expressions of Beclin-1 and LC3B II/LC3B I. The expression of p-AMPK was up-regulated and p-mTOR1 was inhibited, which promoted the nucleation of transcription factor EB (TFEB), leading to autophagy. Moreover, fucoidan induced apoptosis of pancreatic tissue cells. The levels of cleaved caspase-9, cleaved caspase-3, and Bax were up-regulated after fucoidan treatment.
Conclusion: Fucoidan could maintain pancreatic homeostasis and restore immune disorder through enhancing autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR1/TFEB pathway in pancreatic cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Autophagy; Fucoidan; NOD mice; Type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fucoidan prevent murine autoimmune diabetes via suppression TLR4-signaling pathways, regulation DC/Treg induced immune tolerance and improving gut microecology.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019 Dec 16;16:87. doi: 10.1186/s12986-019-0392-1. eCollection 2019. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31889967 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Effects of Fucoidan Via Apoptotic and Autophagic Induction on HSC-3 Oral Squamous CellCarcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Aug 1;21(8):2469-2477. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.8.2469. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32856880 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic and Immunoregulatory Activities of Extract of Phyllanthus emblica L. in NOD with Spontaneous and Cyclophosphamide-Accelerated Diabetic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 8;24(12):9922. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129922. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373070 Free PMC article.
-
Tangzhiqing decoction attenuates cognitive dysfunction of mice with type 2 diabetes by regulating AMPK/mTOR autophagy signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117536. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117536. Epub 2023 Dec 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38056539
-
Total coumarins from Urtica dentata Hand prevent murine autoimmune diabetes via suppression of the TLR4-signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Mar 7;146(1):379-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Jan 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23340441
Cited by
-
Marine Compounds and Age-Related Diseases: The Path from Pre-Clinical Research to Approved Drugs for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes.Mar Drugs. 2024 May 3;22(5):210. doi: 10.3390/md22050210. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38786601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Salpea P, Karuranga S, Petersohn I, Malanda B, Gregg EW, et al. Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20-79 years old adults, 2019 estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162:108086. - PubMed
-
- Loretelli C, Assi E, Seelam AJ, Ben Nasr M, Fiorina P. Cell therapy for type 1 diabetes. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020;20:887–897. - PubMed
-
- Lucier J, Weinstock RS. Diabetes mellitus type 1. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
-
- Bluestone JA, Buckner JH, Herold KC. Immunotherapy: Building a bridge to a cure for type 1 diabetes. Science. 2021;373:510–516. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
