Gordon Holmes Syndrome Model Mice Exhibit Alterations in Microglia, Age, and Sex-Specific Disruptions in Cognitive and Proprioceptive Function
- PMID: 38164552
- PMCID: PMC10849025
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0074-23.2023
Gordon Holmes Syndrome Model Mice Exhibit Alterations in Microglia, Age, and Sex-Specific Disruptions in Cognitive and Proprioceptive Function
Abstract
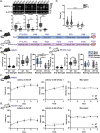
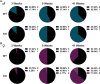
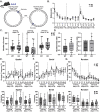
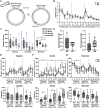
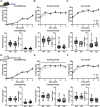
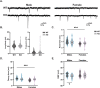
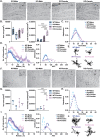
Gordon Holmes syndrome (GHS) is a neurological disorder associated with neuroendocrine, cognitive, and motor impairments with corresponding neurodegeneration. Mutations in the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF216 are strongly linked to GHS. Previous studies show that deletion of Rnf216 in mice led to sex-specific neuroendocrine dysfunction due to disruptions in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. To address RNF216 action in cognitive and motor functions, we tested Rnf216 knock-out (KO) mice in a battery of motor and learning tasks for a duration of 1 year. Although male and female KO mice did not demonstrate prominent motor phenotypes, KO females displayed abnormal limb clasping. KO mice also showed age-dependent strategy and associative learning impairments with sex-dependent alterations of microglia in the hippocampus and cortex. Additionally, KO males but not females had more negative resting membrane potentials in the CA1 hippocampus without any changes in miniature excitatory postsynaptic current (mEPSC) frequencies or amplitudes. Our findings show that constitutive deletion of Rnf216 alters microglia and neuronal excitability, which may provide insights into the etiology of sex-specific impairments in GHS.
Keywords: Gordon Holmes syndrome; RNF216; ataxia; cognitive; microglia; ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2024 George et al.
Figures

References
-
- Bordi F, LeDoux JE (1994) Response properties of single units in areas of rat auditory thalamus that project to the amygdala. II. Cells receiving convergent auditory and somatosensory inputs and cells antidromically activated by amygdala stimulation. Exp Brain Res 98:275–286. 10.1007/BF00228415 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
