Striatal Neurons Are Recruited Dynamically into Collective Representations of Self-Initiated and Learned Actions in Freely Moving Mice
- PMID: 38164559
- PMCID: PMC11057506
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0315-23.2023
Striatal Neurons Are Recruited Dynamically into Collective Representations of Self-Initiated and Learned Actions in Freely Moving Mice
Abstract
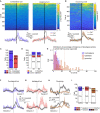
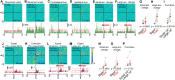
Striatal spiny projection neurons are hyperpolarized-at-rest (HaR) and driven to action potential threshold by a small number of powerful inputs-an input-output configuration that is detrimental to response reliability. Because the striatum is important for habitual behaviors and goal-directed learning, we conducted a microendoscopic imaging in freely moving mice that express a genetically encoded Ca2+ indicator sparsely in striatal HaR neurons to evaluate their response reliability during self-initiated movements and operant conditioning. The sparse expression was critical for longitudinal studies of response reliability, and for studying correlations among HaR neurons while minimizing spurious correlations arising from contamination by the background signal. We found that HaR neurons are recruited dynamically into action representation, with distinct neuronal subsets being engaged in a moment-by-moment fashion. While individual neurons respond with little reliability, the population response remained stable across days. Moreover, we found evidence for the temporal coupling between neuronal subsets during conditioned (but not innate) behaviors.
Keywords: basal ganglia; calcium imaging; correlations; parvalbumin-positive fast-spiking interneurons; population coding; spiny projection neurons.
Copyright © 2024 Tiroshi et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ensemble encoding of action speed by striatal fast-spiking interneurons.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Sep;224(7):2567-2576. doi: 10.1007/s00429-019-01908-7. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 31243530 Free PMC article.
-
Representation of the body in the lateral striatum of the freely moving rat: Fast Spiking Interneurons respond to stimulation of individual body parts.Brain Res. 2017 Feb 15;1657:101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.11.033. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 27914882 Free PMC article.
-
Inversely Active Striatal Projection Neurons and Interneurons Selectively Delimit Useful Behavioral Sequences.Curr Biol. 2018 Feb 19;28(4):560-573.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.031. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29429614 Free PMC article.
-
Spike-timing dependent plasticity in striatal interneurons.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Apr;60(5):780-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.023. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21262240 Review.
-
Excitatory extrinsic afferents to striatal interneurons and interactions with striatal microcircuitry.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Mar;49(5):593-603. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13881. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 29480942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aertsen AMHJ, Gerstein GL, Habib MK, Palm G (1989) Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: modulation of “effective connectivity”. J Neurophysiol 61:900–917. - PubMed
-
- Aosaki T, Kimura M, Graybiel AM (1995) Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Tonically Active Neurons of the Primate’s Striatum.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
