A Constitutive EGFR Kinase Dimer to Study Inhibitor Pharmacology
- PMID: 38164587
- PMCID: PMC10794983
- DOI: 10.1124/molpharm.123.000768
A Constitutive EGFR Kinase Dimer to Study Inhibitor Pharmacology
Abstract
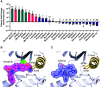
Lung cancer is commonly caused by activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Allosteric kinase inhibitors are unaffected by common ATP-site resistance mutations and represent a promising therapeutic strategy for targeting drug-resistant EGFR variants. However, allosteric inhibitors are antagonized by kinase dimerization, and understanding this phenomenon has been limited to cellular experiments. To facilitate the study of allosteric inhibitor pharmacology, we designed and purified a constitutive EGFR kinase dimer harboring the clinically relevant L858R/T790M mutations. Kinetic characterization revealed that the EGFR kinase dimer is more active than monomeric EGFR(L858R/T790M) kinase and has the same Km,ATP Biochemical profiling of a large panel of ATP-competitive and allosteric EGFR inhibitors showed that allosteric inhibitor potency decreased by >500-fold in the kinase dimer compared with monomer, yielding IC50 values that correlate well with Ba/F3 cellular potencies. Thus, this readily purifiable constitutive asymmetric EGFR kinase dimer represents an attractive tool for biochemical evaluation of EGFR inhibitor pharmacology, in particular for allosteric inhibitors. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Drugs targeting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase are commonly used to treat lung cancers but are affected by receptor dimerization. Here, we describe a locked kinase dimer that can be used to study EGFR inhibitor pharmacology.
Copyright © 2024 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors.Nature. 2016 Jun 2;534(7605):129-32. doi: 10.1038/nature17960. Epub 2016 May 25. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27251290 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant-Selective Allosteric EGFR Degraders are Effective Against a Broad Range of Drug-Resistant Mutations.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Aug 17;59(34):14481-14489. doi: 10.1002/anie.202003500. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32510788 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivities to various epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors of uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations L861Q and S768I: What is the optimal epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor?Cancer Sci. 2016 Aug;107(8):1134-40. doi: 10.1111/cas.12980. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27240419 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting EGFRL858R/T790M and EGFRL858R/T790M/C797S resistance mutations in NSCLC: Current developments in medicinal chemistry.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(5):1550-1581. doi: 10.1002/med.21488. Epub 2018 Jan 26. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29377179 Review.
-
Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):593. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020593. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carey KD, Garton AJ, Romero MS, Kahler J, Thomson S, Ross S, Park F, Haley JD, Gibson N, Sliwkowski MX (2006) Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer Res 66:8163–8171. - PubMed
-
- Du Z, Brown BP, Kim S, Ferguson D, Pavlick DC, Jayakumaran G, Benayed R, Gallant JN, Zhang YK, Yan Y, et al. (2021) Structure-function analysis of oncogenic EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication reveals insights into activation and a potential approach for therapeutic targeting. Nat Commun 12:1382. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gallant JN, Sheehan JH, Shaver TM, Bailey M, Lipson D, Chandramohan R, Red Brewer M, York SJ, Kris MG, Pietenpol JA, et al. (2015) EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication (EGFR -KDD) is a Novel Oncogenic Driver in Lung Cancer that is Clinically Responsive to Afatinib. Cancer Discov 5:1155–1163. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
