Drug-induced inhibition of HMGA and EZH2 activity as a possible therapy for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 38165007
- PMCID: PMC10936675
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2298027
Drug-induced inhibition of HMGA and EZH2 activity as a possible therapy for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
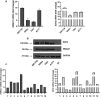
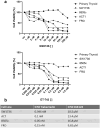
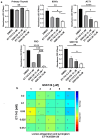
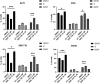
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) is one of the most aggressive and lethal neoplasms in humans, and just limited progresses have been made to extend patient survival and decrease ATC-associated mortality. Thus, the identification of novel therapeutic strategies for treating ATC is needed. Recently, our group has identified two proteins with oncogenic activity, namely HMGA1 and EZH2, with pivotal roles in ATC cancer progression. Therefore, we tested the ability of trabectedin, a HMGA1-targeting drug, and GSK126, an inhibitor of EZH2 enzymatic activity, to impair cell viability of four ATC-derived cell lines. In the present study, we first confirmed the overexpression of HMGA1 and EZH2 in all ATC-derived cell lines and tissues compared to the normal primary thyroid cells and tissues. Then, treatment of the ATC cell lines with trabectedin and GSK126 resulted in a drastic induction of apoptotic cell death, which increased when the ATC cell lines were treated with a combination of both drugs. Conversely, normal primary human thyroid cells did not show any significant reduction in their viability when exposed to the same drugs. Noteworthy, both drugs induced the deregulation of EZH2- and HMGA1-controlled genes. Altogether, these findings propose the combination of trabectedin and GSK126 as possible novel strategy for ATC therapy.
Keywords: EZH2; GSK126; HMGA; Trabectedin; anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validation of EZH2 Inhibitor Efficiency in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Lines.Anticancer Res. 2023 Mar;43(3):1073-1077. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16252. Anticancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36854530
-
Modulation of EZH2 Activity Induces an Antitumoral Effect and Cell Redifferentiation in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7872. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097872. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175580 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 overexpression has a role in the development of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Apr;96(4):1029-38. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1784. Epub 2011 Feb 2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21289264
-
Advances in targeted therapy for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Dec 25;50(6):685-693. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2021-0249. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 35347921 Free PMC article. Review. English.
-
New insights into the mechanisms of the extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 9;14(1):20977. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72020-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39251678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HMGA1 regulates trabectedin sensitivity in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma (STS): A Spanish Group for Research on Sarcomas (GEIS) study.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 May 17;81(1):219. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05250-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38758230 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating gene expression as a strategy to investigate thyroid cancer biology.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Nov 6;68(Spec Issue):e240073. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2024-0073. eCollection 2024. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39876973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complicated crosstalk between HMGA and non-coding RNAs modulates hallmarks of cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Mar 7;25(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03713-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40055693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bai Y, Kakudo K, Jung CK.. Updates in the pathologic classification of thyroid neoplasms: a review of the world health organization classification. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020. Dec;35(4):696–715. PubMed PMID: 33261309; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7803616. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.807 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
