Biology-driven therapy advances in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
- PMID: 38165032
- PMCID: PMC10760962
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI174013
Biology-driven therapy advances in high-grade serous ovarian cancer
Abstract
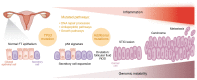
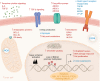
Following a period of slow progress, the completion of genome sequencing and the paradigm shift relative to the cell of origin for high grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) led to a new perspective on the biology and therapeutic solutions for this deadly cancer. Experimental models were revisited to address old questions, and improved tools were generated. Additional pathways emerging as drivers of ovarian tumorigenesis and key dependencies for therapeutic targeting, in particular, VEGF-driven angiogenesis and homologous recombination deficiency, were discovered. Molecular profiling of histological subtypes of ovarian cancer defined distinct genetic events for each entity, enabling the first attempts toward personalized treatment. Armed with this knowledge, HGSOC treatment was revised to include new agents. Among them, PARP inhibitors (PARPis) were shown to induce unprecedented improvement in clinical benefit for selected subsets of patients. Research on mechanisms of resistance to PARPis is beginning to discover vulnerabilities and point to new treatment possibilities. This Review highlights these advances, the remaining challenges, and unsolved problems in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures