Type IV optic nerve and Onodi cell: is there a risk of injury during sphenoid sinus surgery?
- PMID: 38165204
- PMCID: PMC10914358
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2462
Type IV optic nerve and Onodi cell: is there a risk of injury during sphenoid sinus surgery?
Abstract
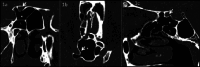
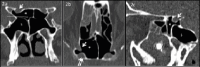
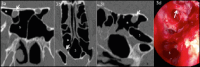
Objective: This study aims to determine the prevalence and types of Onodi cells through computed tomography and investigate the relationship between Onodi cell and the surrounding structures, paying particular attention to the risky proximity to the optic nerve canal.
Methods: In this study, 430 computed tomography scans of paranasal sinuses were analysed to establish the prevalence and different types of Onodi cells. Furthermore, the relationship between Onodi cell and different patterns of sphenoid sinus pneumatisation and surrounding structures were investigated. Special attention was paid to the relationship between Onodi cell and the optic nerve canal, particularly in cases when the optic nerve canal was bulging by more than 50% into the Onodi cell (Type IV).
Results: The Onodi cell was detected in 21.6% of cases, with the most common being Type I (48.5% right, 54.3% left). Type IV bulging of the optic nerve canal into the Onodi cell was observed in 47.1% of cases on the right side, 41.2% on the left side and bilateral in 11.7% of cases.
Conclusions: In our series, we observed a high prevalence of Type IV optic nerve bulging into the Onodi cell. For this reason, we suggest that clinicians should always try to identify it in a pre-operative setting with computed tomography to avoid catastrophic consequences during endoscopic sinus surgery approaching the sphenoid area.
Keywords: Onodi cell; computed tomography; endoscopic sinus surgery; optic nerve; sphenoid sinus.
Copyright © 2024 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This research did not receive any specific grant from fund-ing agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is there a relationship between Onodi cell and optic canal?Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Apr;276(4):1057-1064. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05284-0. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30617426
-
The prevalence of the Onodi cell - Most suitable method of CT evaluation in its detection.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Jun;97:202-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28483236
-
Carotid canal and optic canal at sphenoid sinus.Neurosurg Rev. 2019 Jun;42(2):519-529. doi: 10.1007/s10143-018-0995-4. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Neurosurg Rev. 2019. PMID: 29926302
-
Identification of Onodi cell and new classification of sphenoid sinus for endoscopic sinus surgery.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Nov;5(11):1068-76. doi: 10.1002/alr.21567. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 26097234 Review.
-
Sphenoid sinuses: pneumatisation and anatomical variants-what the radiologist needs to know and report to avoid intraoperative complications.Surg Radiol Anat. 2020 Sep;42(9):1013-1024. doi: 10.1007/s00276-020-02490-y. Epub 2020 May 11. Surg Radiol Anat. 2020. PMID: 32394118 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal trends of blood eosinophilia in severe uncontrolled CRSwNP treated with dupilumab: a real-life study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 May;281(5):2429-2440. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08417-8. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38157036
-
A new CBCT-based classification of posterior extramural ethmoid cells.Surg Radiol Anat. 2025 Jul 16;47(1):173. doi: 10.1007/s00276-025-03686-w. Surg Radiol Anat. 2025. PMID: 40670633
-
Do Onodi Cells Influence the Onset of Sphenoiditis? A Multicentric Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Med. 2025 May 16;14(10):3508. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103508. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Onodi A. The optic nerve and the accessory sinuses of the nose. Der Sehnerv and die NebenOhlen der Nase. Wien, Germany: Alfred Holder; 1907. pp. 1-6.
-
- Özdemir A, Bayar Muluk N, Asal N, et al. . Is there a relationship between Onodi cell and optic canal? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2019;276:1057-1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05284-0 10.1007/s00405-019-05284-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ali IK, Sansare K, Karjodkar F, et al. . Imaging analysis of Onodi cells on cone-beam computed tomography. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2020;24:E319-E322. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1698779 10.1055/s-0039-1698779 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chmielik LP, Chmielik A. The prevalence of the Onodi cell – most suitable method of CT evaluation in its detection. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2017;97:202-205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.04.001 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.04.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Driben JS, Bolger WE, Robles HA, et al. . The reliability of computerized tomographic detection of the Onodi (Sphenoethmoid) cell. Am J Rhinol 1998;12:105-111. https://doi.org/10.2500/105065898781390325 10.2500/105065898781390325 - DOI - PubMed

