Radiologic Features of Nodules Attached to the Mediastinal or Diaphragmatic Pleura at Low-Dose CT for Lung Cancer Screening
- PMID: 38165250
- PMCID: PMC10831475
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.231219
Radiologic Features of Nodules Attached to the Mediastinal or Diaphragmatic Pleura at Low-Dose CT for Lung Cancer Screening
Abstract
Background Pulmonary noncalcified nodules (NCNs) attached to the fissural or costal pleura with smooth margins and triangular or lentiform, oval, or semicircular (LOS) shapes at low-dose CT are recommended for annual follow-up instead of immediate workup. Purpose To determine whether management of mediastinal or diaphragmatic pleura-attached NCNs (M/DP-NCNs) with the same features as fissural or costal pleura-attached NCNs at low-dose CT can follow the same recommendations. Materials and Methods This retrospective study reviewed chest CT examinations in participants from two databases. Group A included 1451 participants who had lung cancer that was first present as a solid nodule with an average diameter of 3.0-30.0 mm. Group B included 345 consecutive participants from a lung cancer screening program who had at least one solid nodule with a diameter of 3.0-30.0 mm at baseline CT and underwent at least three follow-up CT examinations. Radiologists reviewed CT images to identify solid M/DP-NCNs, defined as nodules 0 mm in distance from the mediastinal or diaphragmatic pleura, and recorded average diameter, margin, and shape. General descriptive statistics were used. Results Among the 1451 participants with lung cancer in group A, 163 participants (median age, 68 years [IQR, 61.5-75.0 years]; 92 male participants) had 164 malignant M/DP-NCNs 3.0-30.0 mm in average diameter. None of the 164 malignant M/DP-NCNs had smooth margins and triangular or LOS shapes (upper limit of 95% CI of proportion, 0.02). Among the 345 consecutive screening participants in group B, 146 participants (median age, 65 years [IQR, 59-71 years]; 81 female participants) had 240 M/DP-NCNs with average diameter 3.0-30.0 mm. None of the M/DP-NCNs with smooth margins and triangular or LOS shapes were malignant after a median follow-up of 57.8 months (IQR, 46.3-68.1 months). Conclusion For solid M/DP-NCNs with smooth margins and triangular or LOS shapes at low-dose CT, the risk of lung cancer is extremely low, which supports the recommendation of Lung Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2022 for annual follow-up instead of immediate workup. © RSNA, 2024 See also the editorial by Goodman and Baruah in this issue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

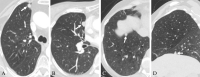
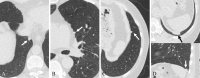
![Flowchart of participants. Group A included participants with
malignant mediastinal or diaphragmatic pleura–attached noncalcified
nodules (M/DP-NCNs) from the Initiative for Early Lung Cancer Research on
Treatment–Mount Sinai Health System (IELCART-MSHS) and the
International Early Lung Cancer Action Program (I-ELCAP). Group B included
participants from a lung cancer (LC) screening program (Mount Sinai I-ELCAP
[MS-ELCAP]) with benign M/DP-NCNs screened at three hospitals within the
Mount Sinai Health System.](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/e9fa/10831475/15402ff5f24b/radiol.231219.fig1.gif)
References
-
- Henschke CI , Yankelevitz DF , Naidich DP , et al. . CT screening for lung cancer: suspiciousness of nodules according to size on baseline scans . Radiology 2004. ; 231 ( 1 ): 164 – 168 . - PubMed
-
- I-ELCAP Investigators . International Early Lung Cancer Action Program: screening protocol . https://www.ielcap.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/ielcap-protocol.pdf. Accessed September 21, 2023 .
-
- Lung CT Screening Reporting & Data System (Lung-RADS) . Version 2022 . American College of Radiology; . https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/Lung-Rads. Accessed September 21, 2023 .
-
- Bueno J , Landeras L , Chung JH . Updated Fleischner Society guidelines for managing incidental pulmonary nodules: common questions and challenging scenarios . RadioGraphics 2018. ; 38 ( 5 ): 1337 – 1350 . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

