In vivo delivery of engineered synthetic DNA-encoded SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies for pre-exposure prophylaxis in non-human primates
- PMID: 38165394
- PMCID: PMC10903752
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2294860
In vivo delivery of engineered synthetic DNA-encoded SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies for pre-exposure prophylaxis in non-human primates
Abstract
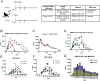
COVID-19 remains a major public health concern. Monoclonal antibodies have received emergency use authorization (EUA) for pre-exposure prophylaxis against COVID-19 among high-risk groups for treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19. In addition to recombinant biologics, engineered synthetic DNA-encoded antibodies (DMAb) are an important strategy for direct in vivo delivery of protective mAb. A DMAb cocktail was synthetically engineered to encode the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains of two different two different Fc-engineered anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The DMAbs were designed to enhance in vivo expression and delivered intramuscularly to cynomolgus and rhesus macaques with a modified in vivo delivery regimen. Serum levels were detected in macaques, along with specific binding to SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain protein and neutralization of multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in pseudovirus and authentic live virus assays. Prophylactic administration was protective in rhesus macaques against signs of SARS-CoV-2 (USA-WA1/2020) associated disease in the lungs. Overall, the data support further study of DNA-encoded antibodies as an additional delivery mode for prevention of COVID-19 severe disease. These data have implications for human translation of gene-encoded mAbs for emerging infectious diseases and low dose mAb delivery against COVID-19.
Keywords: DMAb; DNA; DNA-encoded monoclonal antibody; SARS-CoV-2; gene-encoded antibody; macaque; monoclonal antibody; prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
D.B.W. has received grant funding, participates in industry collaborations, has received speaking honoraria, and has received fees for consulting, including serving on scientific review committees and board series. Remuneration received by D.B.W. includes direct payments and stock or stock options. D.B.W. also discloses the following paid associations with commercial partners: GeneOne (consultant), Geneos (advisory board), AstraZeneca (advisory board, speaker), Inovio (BOD, SRA, Stock), Sanofi (advisory board) and BBI (advisory board). A.J.G, B.S., V.M., B.J.S., B.N., A.G., and T.R.F.S. are employees of Inovio Pharmaceuticals and as such receives salary and benefits, including ownership of stock and stock options. J.R.F, K.R, and M.T.E are employees of and hold or may hold stock in AstraZeneca. All other authors declare no completing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Premkumar L, Segovia-Chumbez B, Jadi R, et al. . The receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein is an immunodominant and highly specific target of antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Sci Immunol. 2020;5(48):eabc8413. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abc8413 PubMed PMID: 32527802; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC7292505. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CDC . COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. [accessed 2022 September]. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
