Enhancing the Functional Performance of Patients with Late-Stage Age-Related Macular Degeneration Implanted with a Miniature Telescope using Rehabilitation Training
- PMID: 38165600
- PMCID: PMC10853143
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-023-00871-1
Enhancing the Functional Performance of Patients with Late-Stage Age-Related Macular Degeneration Implanted with a Miniature Telescope using Rehabilitation Training
Erratum in
-
Correction: Enhancing the Functional Performance of Patients with Late-Stage Age-Related Macular Degeneration Implanted with a Miniature Telescope using Rehabilitation Training.Ophthalmol Ther. 2024 Mar;13(3):709. doi: 10.1007/s40123-024-00890-6. Ophthalmol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38315351 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: In this work, our aim is to report the functional outcomes of cataract surgery with smaller-incision new-generation miniature telescope (SING IMT) implantation followed by rehabilitation training in patients with central visual loss due to late-stage age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
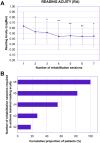
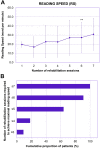
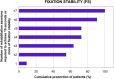
Methods: This retrospective study included patients who were monocularly implanted with SING IMT and then followed a rehabilitation program based on 6 biweekly sessions focused on visual abilities, reading, writing, visual motor integration and mobility. A total of 11 participants were included in this study. Reading acuity (RA), reading speed (RS), and fixation stability (FS) were assessed biweekly at 6-, 8-, 10-, 12-, 14-, and 16-week follow-up visits after SING IMT implantation and at a final assessment at 24 weeks. Best-corrected distance visual acuity (BCDVA) was also measured at baseline and at the same postoperative timepoints.
Results: Mean baseline BCDVA was 12.5 ± 8.6 letter score. Both RA and RS were found to be significantly improved from the first rehabilitation session (6 weeks after surgery) to the last session (24 weeks after surgery). At the end of the rehabilitation program, mean RA was 0.45 ± 0.19 LogMAR and mean RS was 30.9 ± 17.6 words per minute. Moreover, all patients achieved a FS of 15 s or more after the last rehabilitation session. Most patients (55%) achieved an improvement of 15 letters in BCDVA at the end of the study.
Conclusions: This study suggests that rehabilitation training can improve visual functions of patients with late-stage AMD implanted with SING IMT in real-world tasks such as reading skills.
Keywords: Geographic atrophy; Implantable ophthalmic device; Intraocular lens; Late-stage age-related macular degeneration (AMD); Low vision, visual rehabilitation, speed reading, reading acuity, smaller-incision new generation implantable miniature telescope, SING IMT; Visual impairment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Faustino Vidal-Aroca reports being an employee of Samsara Vision during this study. Paola Sasso, Alfonso Savastano, Angelo Maria Minnella, Giuseppe Francione, Leonardo Sammarco, Valentina Cima, Ritangela Ghiraldelli, Roberta Mattei, Stanislao Rizzo have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

