Magnetic resonance imaging techniques for indirect assessment of myelin content in the brain using standard T1w and T2w MRI sequences and postprocessing analysis
- PMID: 38165761
- PMCID: PMC10861246
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.935250
Magnetic resonance imaging techniques for indirect assessment of myelin content in the brain using standard T1w and T2w MRI sequences and postprocessing analysis
Abstract
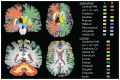
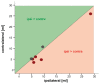
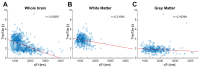
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has revolutionized our ability to non-invasively study the brain's structural and functional properties. However, detecting myelin, a crucial component of white matter, remains challenging due to its indirect visibility on conventional MRI scans. Myelin plays a vital role in neural signal transmission and is associated with various neurological conditions. Understanding myelin distribution and content is crucial for insights into brain development, aging, and neurological disorders. Although specialized MRI sequences can estimate myelin content, these are time-consuming. Also, many patients sent to specialized neurological centers have an MRI of the brain already scanned. In this study, we focused on techniques utilizing standard MRI T1-weighted (T1w) and T2 weighted (T2w) sequences commonly used in brain imaging protocols. We evaluated the applicability of the T1w/T2w ratio in assessing myelin content by comparing it to quantitative T1 mapping (qT1). Our study included 1 healthy adult control and 7 neurologic patients (comprising both pediatric and adult populations) with epilepsy originating from focal epileptogenic lesions visible on MRI structural scans. Following image acquisition on a 3T Siemens Vida scanner, datasets were co registered, and segmented into anatomical regions using the Fastsurfer toolbox, and T1w/T2w ratio maps were calculated in Matlab software. We further assessed interhemispheric differences in volumes of individual structures, their signal intensity, and the correlation of the T1w/T2w ratio to qT1. Our data demonstrate that in situations where a dedicated myelin-sensing sequence such as qT1 is not available, the T1w/T2w ratio provides significantly better information than T1w alone. By providing indirect information about myelin content, this technique offers a valuable tool for understanding the neurobiology of myelin-related conditions using basic brain scans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated separation of diffusely abnormal white matter from focal white matter lesions on MRI in multiple sclerosis.Neuroimage. 2020 Jun;213:116690. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116690. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32119987
-
Use of T1-weighted/T2-weighted magnetic resonance ratio images to elucidate changes in the schizophrenic brain.Brain Behav. 2015 Sep 25;5(10):e00399. doi: 10.1002/brb3.399. eCollection 2015 Oct. Brain Behav. 2015. PMID: 26516617 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping myelin in white matter with T1-weighted/T2-weighted maps: discrepancy with histology and other myelin MRI measures.Brain Struct Funct. 2023 Mar;228(2):525-535. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02600-z. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Brain Struct Funct. 2023. PMID: 36692695 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the dynamic development of the cerebral cortex in childhood and adolescence: Integrating macro- and microstructural MRI findings.Prog Neurobiol. 2021 Sep;204:102109. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102109. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Prog Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34147583 Review.
-
Intensity scaling of conventional brain magnetic resonance images avoiding cerebral reference regions: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0298642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298642. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38483873 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aging Brain from a Lifespan Perspective.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2024;68:349-370. doi: 10.1007/7854_2024_476. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38797799 Review.
