Identification of the feature genes involved in cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19
- PMID: 38165854
- PMCID: PMC10760774
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296030
Identification of the feature genes involved in cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19
Abstract
Objective: Screening of feature genes involved in cytokine release syndrome (CRS) from the coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19).
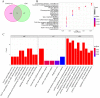
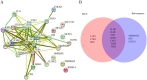
Methods: The data sets related to COVID-19 were retrieved using Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to CRS were analyzed with R software and Venn diagram, and the biological processes and signaling pathways involved in DEGs were analyzed with GO and KEGG enrichment. Core genes were screened using Betweenness and MCC algorithms. GSE164805 and GSE171110 dataset were used to verify the expression level of core genes. Immunoinfiltration analysis was performed by ssGSEA algorithm in the GSVA package. The DrugBank database was used to analyze the feature genes for potential therapeutic drugs.
Results: This study obtained 6950 DEGs, of which 971 corresponded with CRS disease genes (common genes). GO and KEGG enrichment showed that multiple biological processes and signaling pathways associated with common genes were closely related to the inflammatory response. Furthermore, the analysis revealed that transcription factors that regulate these common genes are also involved in inflammatory response. Betweenness and MCC algorithms were used for common gene screening, yielding seven key genes. GSE164805 and GSE171110 dataset validation revealed significant differences between the COVID-19 and normal controls in four core genes (feature genes), namely IL6R, TLR4, TLR2, and IFNG. The upregulated IL6R, TLR4, and TLR2 genes were mainly involved in the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway of the inflammatory pathway, while the downregulated IFNG genes primarily participated in the necroptosis and JAK-STAT signaling pathways. Moreover, immune infiltration analysis indicated that higher expression of these genes was associated with immune cell infiltration that mediates inflammatory response. In addition, potential therapeutic drugs for these four feature genes were identified via the DrugBank database.
Conclusion: IL6R, TLR4, TLR2, and IFNG may be potential pathogenic genes and therapeutic targets for the CRS associated with COVID-19.
Copyright: © 2024 Yang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Blood transcriptome analysis revealed the crosstalk between COVID-19 and HIV.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 28;13:1008653. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1008653. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389792 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic analysis and preliminary validation of potential therapeutic targets for COVID-19 infection in asthma patients.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Dec 27;20(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01010-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36575422 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis to Identify Intersection Genes, Associated Pathways and Therapeutic Drugs between COVID-19 and Oral Candidiasis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(8):1533-1546. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666221007111239. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 36214307
-
Network-Based Data Analysis Reveals Ion Channel-Related Gene Features in COVID-19: A Bioinformatic Approach.Biochem Genet. 2023 Apr;61(2):471-505. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10280-x. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 36104591 Free PMC article.
-
[Exploration of omics mechanism and drug prediction of coronavirus-induced heart failure based on clinical bioinformatics].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 24;48(7):587-592. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20200308-00172. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32228827 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Identification of Hub Genes and Pathways in Preinfusion Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell Products Associated With Cytokine Release Syndrome.Cureus. 2025 Apr 12;17(4):e82155. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82155. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40370902 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Susceptibility in Endothelial Injury Syndromes after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and Other Cellular Therapies: Climbing a Steep Hill.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 May 15;46(5):4787-4802. doi: 10.3390/cimb46050288. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38785556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

