A general approach for inferring the ancestry of recent ancestors of an admixed individual
- PMID: 38165936
- PMCID: PMC10786287
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2316242120
A general approach for inferring the ancestry of recent ancestors of an admixed individual
Abstract
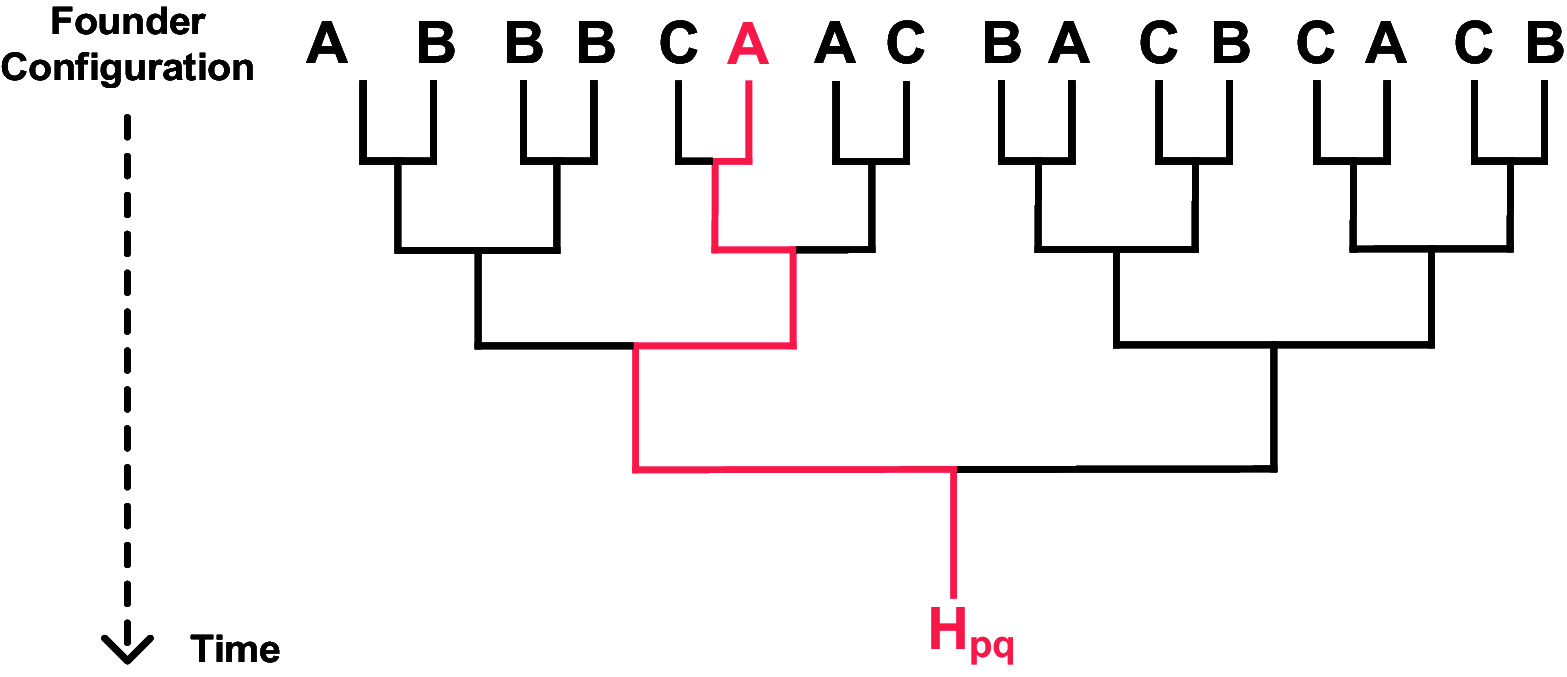
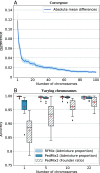
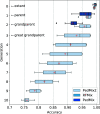
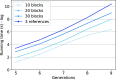
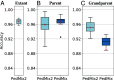
The genome of an individual from an admixed population consists of segments originated from different ancestral populations. Most existing ancestry inference approaches focus on calling these segments for the extant individual. In this paper, we present a general ancestry inference approach for inferring recent ancestors from an extant genome. Given the genome of an individual from a recently admixed population, our method can estimate the proportions of the genomes of the recent ancestors of this individual that originated from some ancestral populations. The key step of our method is the inference of ancestors (called founders) right after the formation of an admixed population. The inferred founders can then be used to infer the ancestry of recent ancestors of an extant individual. Our method is implemented in a computer program called PedMix2. To the best of our knowledge, there is no existing method that can practically infer ancestors beyond grandparents from an extant individual's genome. Results on both simulated and real data show that PedMix2 performs well in ancestry inference.
Keywords: ancestry inference; genetic tests; genetics; population admixture; recombination.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inferring the ancestry of parents and grandparents from genetic data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Aug 14;16(8):e1008065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008065. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32797037 Free PMC article.
-
A statistical model for reference-free inference of archaic local ancestry.PLoS Genet. 2019 May 28;15(5):e1008175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008175. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31136573 Free PMC article.
-
MI-MAAP: marker informativeness for multi-ancestry admixed populations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Apr 3;21(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3462-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32245404 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and challenges of local ancestry in genetic association analyses.Am J Hum Genet. 2025 Apr 3;112(4):727-740. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2025.03.004. Am J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 40185073 Review.
-
Inferring ancestry from population genomic data and its applications.Front Genet. 2014 Jul 3;5:204. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00204. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25071832 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

